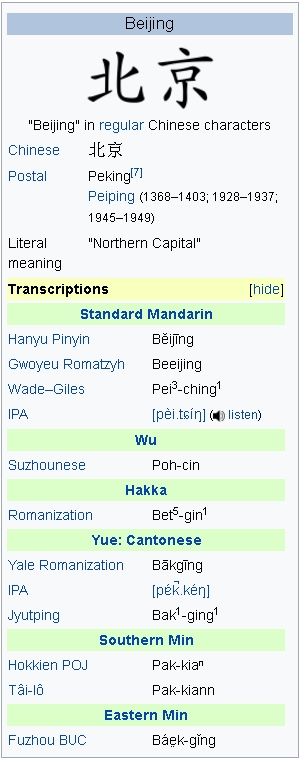
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Beijing : 北京市
Municipality: Beijing Municipality

Clockwise from top: Beijing CBD skyline, Tiananmen, Temple of Heaven, National Center for the Performing Arts, and Beijing National Stadium
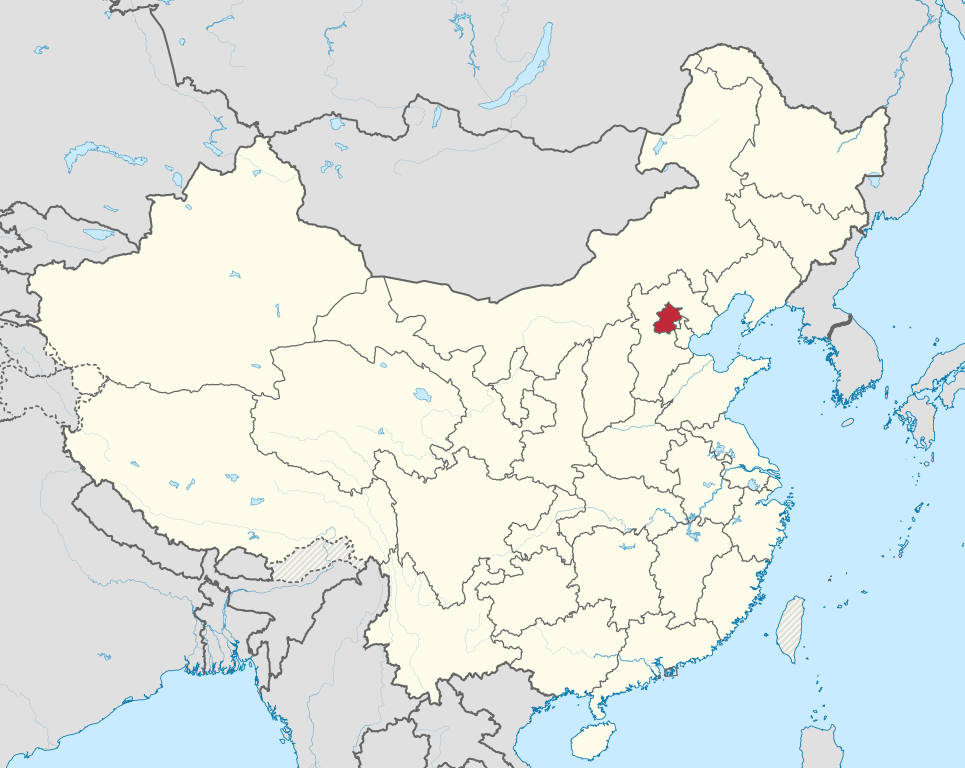
Location of Beijing Municipality within China
Coordinates: 39°55′N 116°23′E
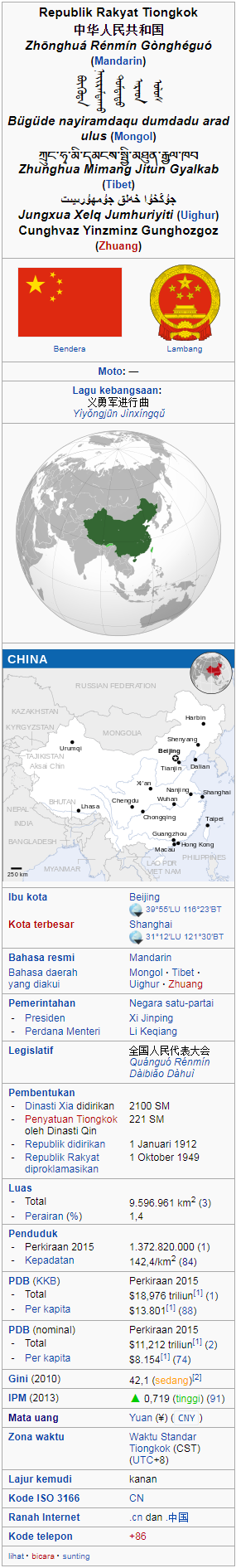
- Country: People’s Republic of China
- Established date: 1046 BC
- Divisions
– County-level: 16 districts
– Township-level: 289 towns and villages
- Government
• Type: Municipality
• Party: Secretary Cai Qi
• Mayor: Chen Jining (acting)
• Congress Chairman: Li Wei
• Conference Chairman: Ji Lin
- Area
• Municipality 16,411 km2 (6,336 sq mi)
• Land 16,801 km2 (6,487 sq mi)
• Urban 1,368 km2 (528 sq mi)
• Rural 15,042 km2 (5,808 sq mi)
- Elevation: 43.5 m (142.7 ft)
- Population: (2015)[3]
• Municipality 21,700,000
• Density 1,300/km2 (3,400/sq mi)
• Urban 18,590,000
• Metro (2010)[4] 24,900,000
• Ranks in China Population: 27th;
- Density: 4th
- Major ethnic groups
• Han 95%
• Manchu 2%
• Hui 2%
• Mongol 0.3%
• Other 0.7%
- Time zone: CST (UTC+8)
- Postal code: 100000–102629
- Area code(s) 10
- GDP (nominal) 2016
– Total CNY 2.49 trillion
- USD 375 billion (13th)
– Per capita CNY 114,742
- USD 17,278 (2nd)
– Growth Increase 6.7%
- HDI (2014) 0.869 (1st)—very high
- License plate prefixes:
- 京A, C, E, F, H, J, K, L, M, N, P, Q
- 京B (taxis)
- 京G, Y (outside urban area)
- 京O, D (police and authorities)
- Abbreviation: BJ / 京 (jīng)
- City trees: Chinese arborvitae (Platycladus orientalis)
- Pagoda tree: (Sophora japonica)
- City flowers:
- China rose (Rosa chinensis)
- Chrysanthemum (Chrysanthemum morifolium)
Beijing, (/beɪˈdʒɪŋ/) formerly romanized as Peking, is the capital of the People’s Republic of China and the world’s second most populous city proper and most populous capital city. The city, located in northern China, is governed as a direct-controlled municipality under the national government with 16 urban, suburban, and rural districts. Beijing Municipality is surrounded by Hebei Province with the exception of neighbouring Tianjin Municipality to the southeast; together the three divisions form the Jingjinji metropolitan region and the national capital region of China.
As a city combining both modern and traditional architecture, Beijing is an ever-changing megacity rich in history but also truly modern, exemplified in its global influence in politics, business & economy, education, history, culture, language, music, sporting, architecture, civilization, fashion, art, entertainment, innovation, and technology. Beijing is the second largest Chinese city by urban population after Shanghai and is the nation’s political, cultural, and educational center. It is home to the headquarters of most of China’s largest state-owned companies and is a major hub for the national highway, expressway, railway, and high-speed rail networks. The Beijing Capital International Airport has been the second busiest in the world by passenger traffic since 2010, and, as of 2016, the city’s subway network is the busiest and second longest in the world, after Shanghai’s subway system.
The city’s history dates back three millennia. As the last of the Four Great Ancient Capitals of China, Beijing has been the political center of the country for much of the past eight centuries. With mountains surrounding the inland city on three sides, in addition to the old inner and outer city walls, Beijing was strategically poised and developed to be the residence of the emperor and thus was the perfect location for the imperial capital. Beijing was the largest city in the world by population for much of the second millennium A.D. The city is renowned for its opulent palaces, temples, parks, gardens, tombs, walls and gates. Its art treasures and universities have made it center of culture and art in China. Encyclopædia Britannica notes that “few cities in the world have served for so long as the political headquarters and cultural centre of an area as immense as China.” Beijing has seven UNESCO World Heritage Sites – the Forbidden City, Temple of Heaven, Summer Palace, Ming Tombs, Zhoukoudian, as well as parts of the Great Wall and the Grand Canal, all popular locations for tourism. Siheyuans, the city’s traditional housing style, and hutongs, the narrow alleys between siheyuans, are major tourist attractions and are common in urban Beijing. The city hosted the 2008 Summer Olympics and was chosen to host the 2022 Winter Olympics, making it the first city to ever host both Winter and Summer Olympics.
Many of Beijing’s 91 universities consistently rank among the best in China, of which Peking University and Tsinghua University are ranked in the top 60 universities of the world. In 2015, 52 companies of the Fortune Global 500 company headquarters were located in Beijing, more than any other city in the world, including state-owned enterprises State Grid, China National Petroleum, and Sinopec Group, ranked 2nd, 3rd, and 4th, respectively. Beijing CBD is quickly becoming the center for Beijing’s economic expansion, rapid modernization, and radically changing skyline, with the ongoing or recently completed construction of multiple skyscrapers. Beijing’s Zhongguancun area is also known as China’s Silicon Valley and China’s center of innovation and technology entrepreneurship. According to the 2016 InterNations Expat Insider Survey, Beijing ranked first in Asia in the subcategory “Personal Finance Index,” a measure of expats’ salaries versus cost of living in the city. Expats live primarily in urban districts such as Dongcheng and Chaoyang in the east, or in suburban districts such as Shunyi.
Contents
1 Etymology
2 History
2.1 Early history
2.2 Early Imperial China
2.3 Ming dynasty
2.4 Qing dynasty
2.5 Republic of China
2.6 People’s Republic of China
3 Geography
3.1 Climate
3.2 Environmental problems
4 Politics and government
4.1 Administrative divisions
4.2 Judiciary and procuracy
4.3 Diplomatic missions
5 Economy
5.1 Sector composition
5.2 Economic zones
6 Demographics
7 Culture
7.1 Places of interest
7.2 Architecture
7.3 Religion
8 Media
8.1 Television and radio
8.2 Press
9 Sports
9.1 Events
9.2 Venues
9.3 Clubs
10 Transportation
10.1 Rail and high-speed rail
10.2 Roads and expressways
10.3 Air
10.4 Public transit
10.5 Taxi
10.6 Bicycles
11 Defense and aerospace
12 Nature and wildlife
1 | Etymology
Over the past 3,000 years, the city of Beijing has had numerous other names. The name Beijing, which means “Northern Capital” (from the Chinese characters 北 for north and 京 for capital), was applied to the city in 1403 during the Ming Dynasty to distinguish the city from Nanjing (the “Southern Capital”). The English spelling is based on the pinyin romanization of the two characters as they are pronounced in Standard Mandarin. An older English spelling, Peking, is the postal romanization of the same two characters as they are pronounced in Chinese dialects spoken in the southern port towns first visited by European traders and missionaries. Those dialects preserve the Middle Chinese pronunciation of 京 as kjaeng, prior to a phonetic shift in the northern dialects to the modern pronunciation. Although Peking is no longer the common name for the city, some of the city’s older locations and facilities, such as Beijing Capital International Airport, with IATA Code PEK, and Peking University, still use the former romanization.
The single Chinese character abbreviation for Beijing is 京, which appears on automobile license plates in the city. The official Latin alphabet abbreviation for Beijing is “BJ”.
2 | History
2.1 | Early History
The earliest traces of human habitation in the Beijing municipality were found in the caves of Dragon Bone Hill near the village of Zhoukoudian in Fangshan District, where Peking Man lived. Homo erectus fossils from the caves date to 230,000 to 250,000 years ago. Paleolithic Homo sapiens also lived there more recently, about 27,000 years ago. Archaeologists have found neolithic settlements throughout the municipality, including in Wangfujing, located in downtown Beijing.
The first walled city in Beijing was Ji, a city from the 11th to 7th century BC. Within modern Beijing, Ji was located around the present Guang’anmen area in the south of Xicheng District. This settlement was later conquered by the state of Yan and made its capital under the name Yanjing.
2.2 | Early Imperial China
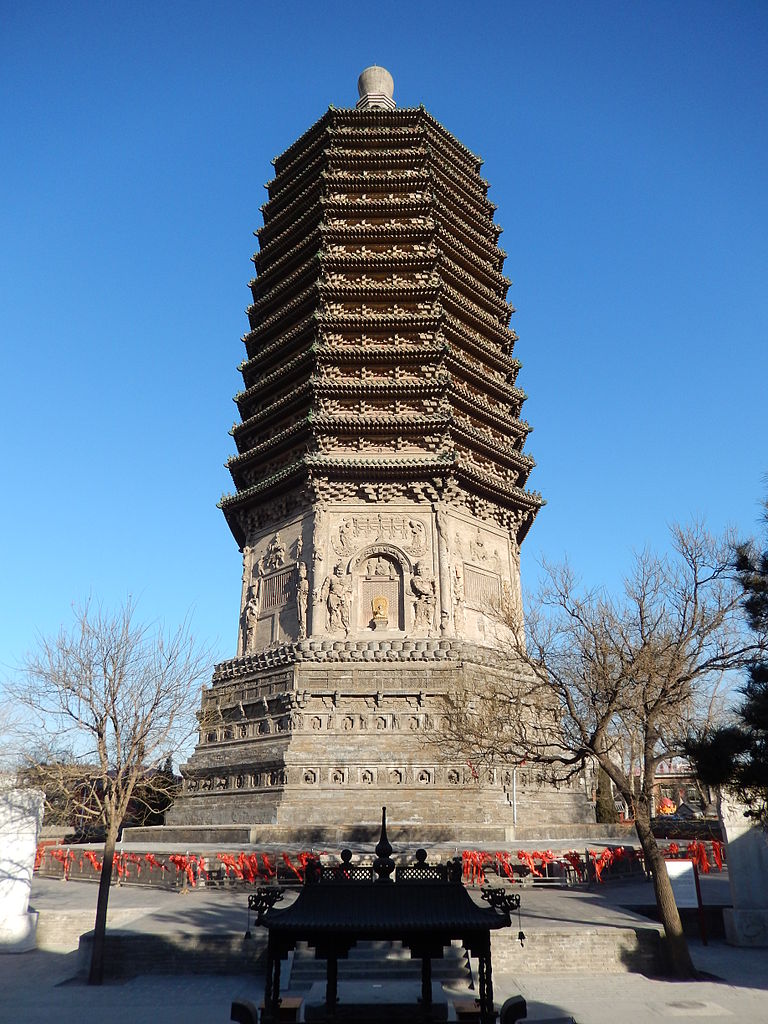

The Tianning Pagoda, built around 1120 during the Liao dynasty.
After the First Emperor unified China, Beijing became a prefectural capital for the region. During the Three Kingdoms period, it was held by Gongsun Zan and Yuan Shao before falling to Cao Cao’s Wei Kingdom. The AD 3rd-century Western Jin demoted the town, placing the prefectural seat in neighbouring Zhuozhou.
During the Sixteen Kingdoms period when northern China was conquered and divided by the Wu Hu, Beijing, as Jicheng, was briefly the capital of the Xianbei Former Yan Kingdom.
After China was reunified during the Sui Dynasty, Beijing, known as Zhuojun, became the northern terminus of the Grand Canal. Under the Tang Dynasty, Beijing as Fanyang, served as a military frontier command center. During the An-Shi Rebellion and again amidst the turmoil of the late Tang, local military commanders founded their own short-lived Yan Dynasties and called the city Yanjing, or the “Yan Capital.” In 938, after the fall of the Tang, the Later Jin ceded the entire northern frontier to the Khitan Liao Dynasty, which renamed the city Nanjing, or the “Southern Capital”, one of four secondary capitals to complement its “Supreme Capital”, Shangjing (modern Baarin Left Banner in Inner Mongolia). Some of the oldest surviving structures in Beijing date to the Liao period, including the Tianning Pagoda.
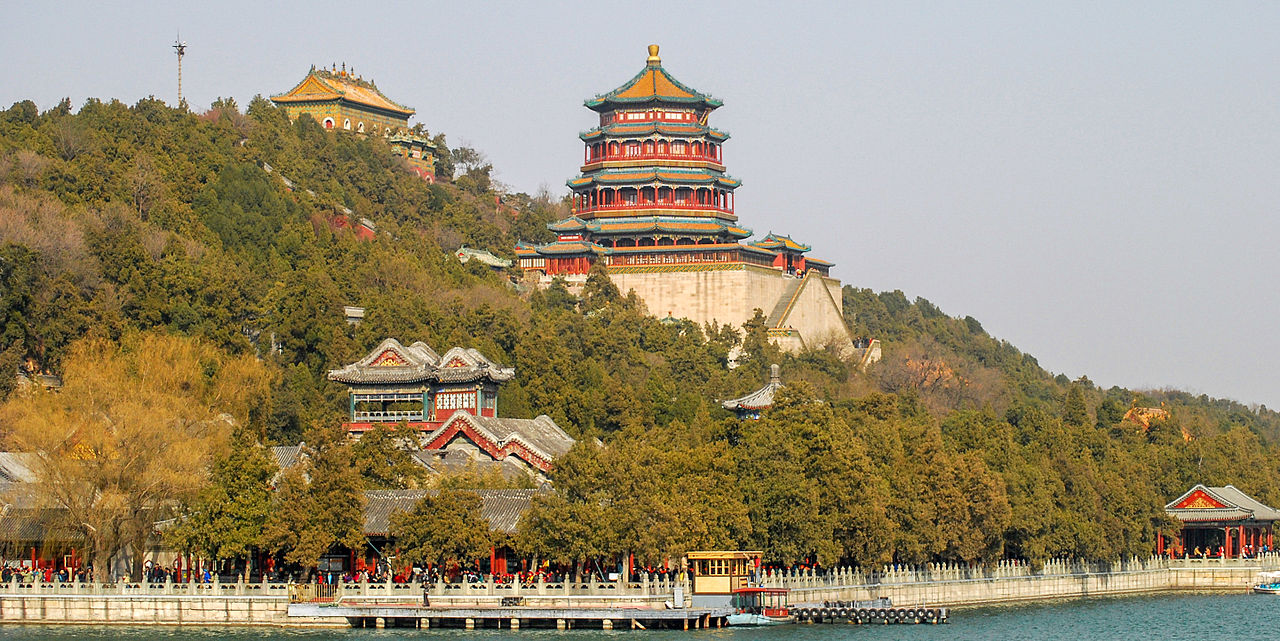

Longevity Hill in Beijing where Kublai Khan wrote his poem.
The Liao fell to the Jurchen Jin dynasty in 1122, which gave the city to the Song Dynasty and then retook it in 1125 during its conquest of northern China. In 1153, the Jurchen Jin made Beijing their “Central Capital”, called Zhongdu. The city was besieged by Genghis Khan’s invading Mongolian army in 1213 and razed to the ground two years later. Two generations later, Kublai Khan ordered the construction of Dadu (or Daidu to the Mongols, commonly known as Khanbaliq), a new capital for his Yuan dynasty to be located adjacent to the Jurchen Jin ruins. The construction took from 1264 to 1293, but greatly enhanced the status of a city on the northern fringe of China proper. The city was centered on the Drum Tower slightly to the north of modern Beijing and stretched from the present-day Chang’an Avenue to the Line 10 subway. Remnants of the Yuan rammed earth wall still stand and are known as the Tucheng.
2.3 | Ming Dynasty
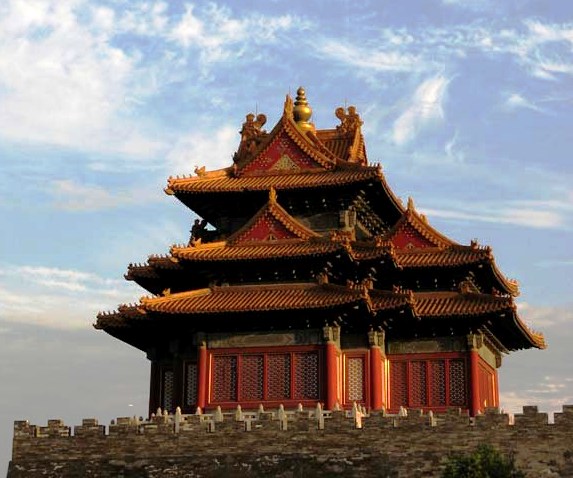

One of the corner towers of the Forbidden City.
In 1368, soon after declaring the new Hongwu era of the Ming dynasty, the rebel leader Zhu Yuanzhang sent an army to Khanbaliq and conquered it. Since the Yuan continued to occupy Shangdu and Mongolia, however, a new town was established to supply the military garrisons in the area. This was called Beiping and under the Hongwu Emperor’s feudal policies it was given to Zhu Di, one of his sons, who was created “Prince of Yan”.
The early death of Zhu Yuanzhang’s heir led to a succession struggle on his death, one that ended with the victory of Zhu Di and the declaration of the new Yongle era. Since his harsh treatment of the Ming capital Yingtian (modern Nanjing) alienated many there, he established his fief as a new co-capital. The city of Beiping became Shuntian in 1403. The construction of the new imperial residence, the Forbidden City, took from 1406 to 1420; this period was also responsible for several other of the modern city’s major attractions, such as the Temple of Heaven and Tian’anmen (although the square facing it was not cleared until 1651). On 28 October 1420, the city was officially designated the capital of the Ming Dynasty in the same year that the Forbidden City was completed. Beijing became the empire’s primary capital (Jingshi) and Yingtian – or called Nanjing – became the co-capital. (A 1425 order by Zhu Di’s son, the Hongxi Emperor, to return the capital to Nanjing was never carried out: he died, probably of a heart attack, the next month. He was buried, like almost every Ming emperor to follow him, in an elaborate necropolis to Beijing’s north.)
By the 15th century, Beijing had essentially taken its current shape. The Ming city wall continued to serve until modern times, when it was pulled down and the 2nd Ring Road was built in its place. It is generally believed that Beijing was the largest city in the world for most of the 15th, 16th, 17th, and 18th centuries. The first known church was constructed by Catholics in 1652 at the former site of Matteo Ricci’s chapel; the modern Nantang Cathedral was later built upon the same site.
The capture of Beijing by Li Zicheng’s peasant army in 1644 ended the dynasty, but he and his Shun court abandoned the city without a fight when the Manchu army of Prince Dorgon arrived 40 days later.
2.4 | Qing Dynasty
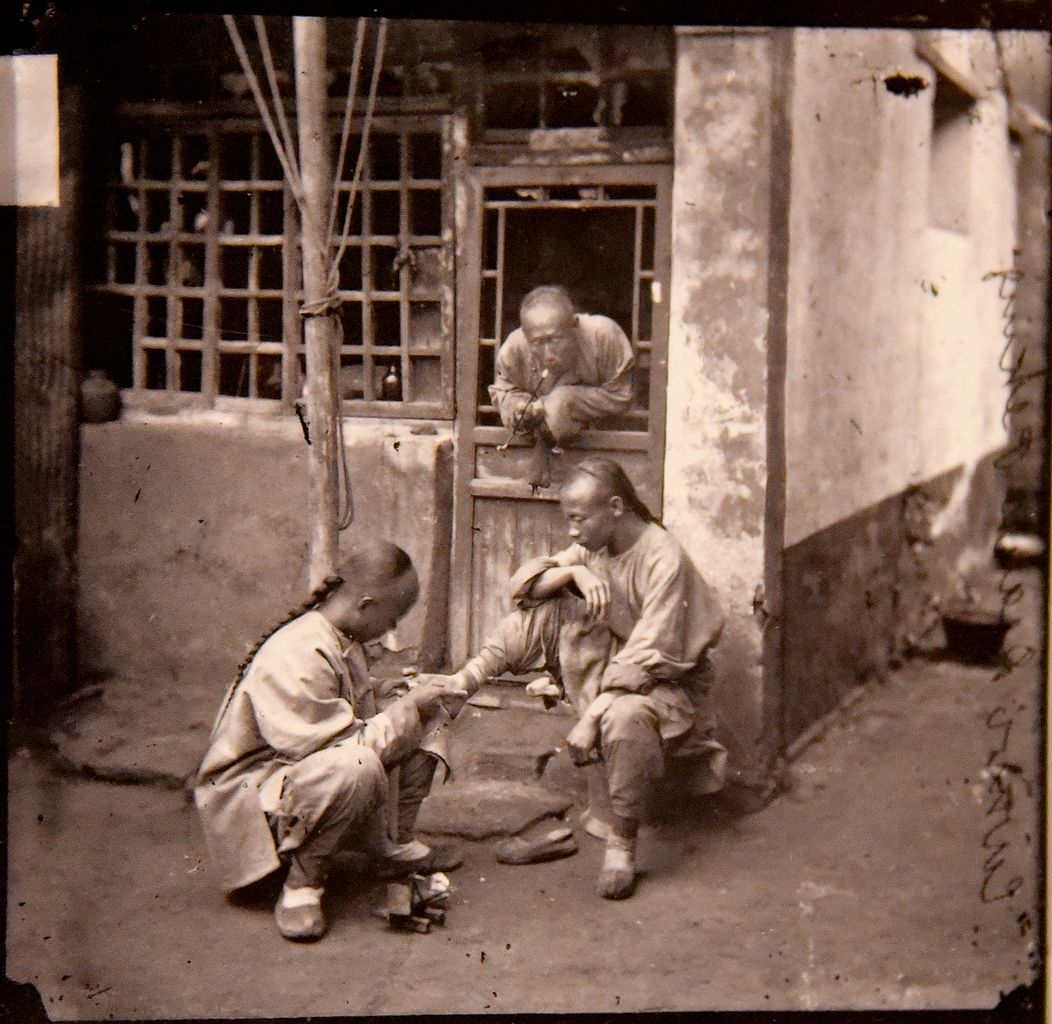

A Pekingese chiropodist. John Thomson. China,1869. The Wellcome Collection, London
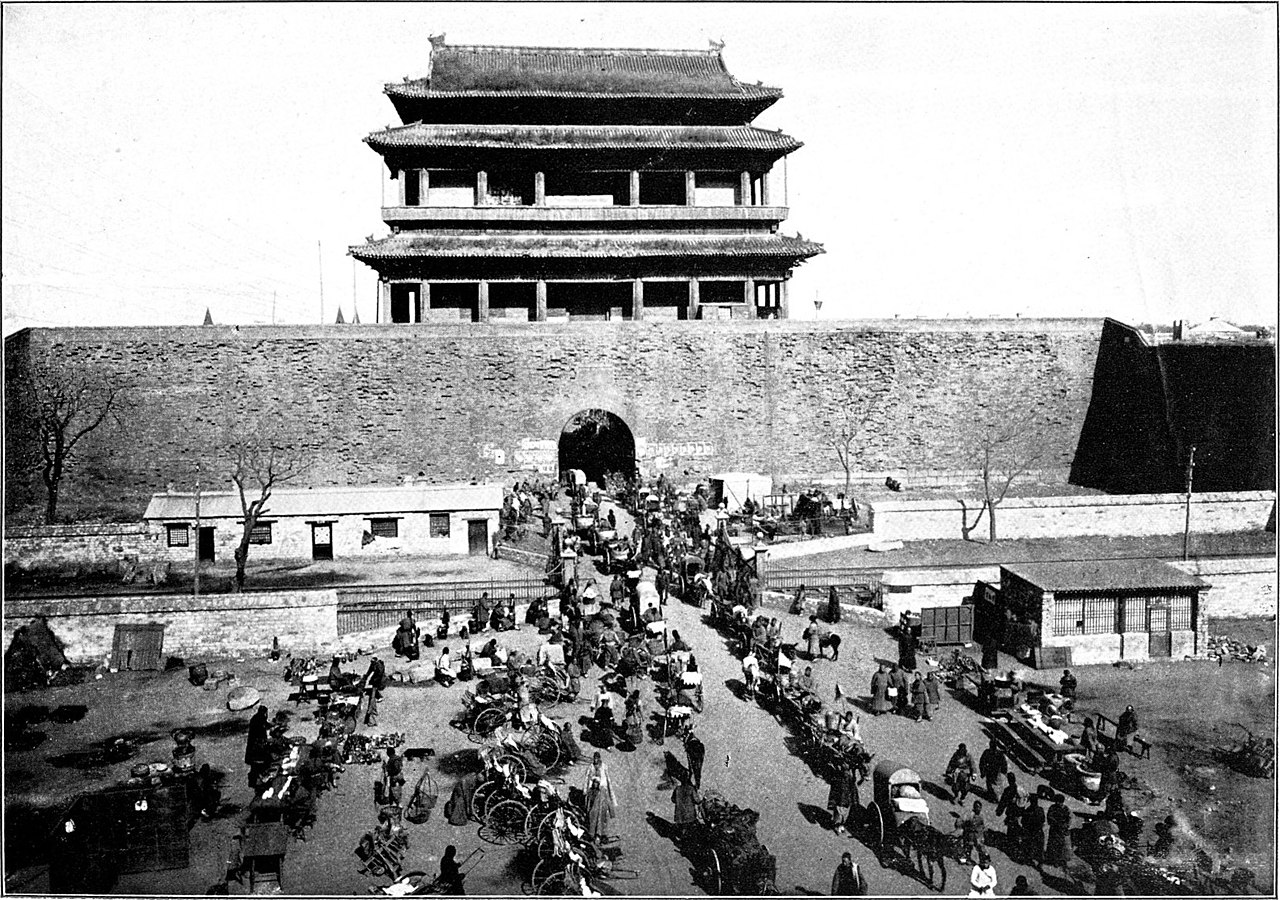

Chongwenmen, a gate to the inner walled city, c. 1906
Dorgon established the Qing Dynasty as a direct successor of the Ming (delegitimising Li Zicheng and his followers) and Beijing became China’s sole capital. The Qing emperors made some modifications to the Imperial residence but, in large part, the Ming buildings and the general layout remained unchanged. Facilities for Manchu worship were introduced, but the Qing also continued the traditional state rituals. Signage was bilingual or Chinese. This early Qing Beijing later formed the setting for the Chinese novel Dream of the Red Chamber.
During the Second Opium War, Anglo-French forces captured the city, looting and burning the Old Summer Palace in 1860. Under the Convention of Peking ending that war, Western powers for the first time secured the right to establish permanent diplomatic presences within the city. In 1900, the attempt by the “Boxers” to eradicate this presence, as well as Chinese Christian converts, led to Beijing’s reoccupation by foreign powers. During the fighting, several important structures were destroyed, including the Hanlin Academy and the (new) Summer Palace.
2.5 | Republic of China
The fomenters of the Xinhai Revolution of 1911 sought to replace Qing rule with a republic and leaders like Sun Yat-sen originally intended to return the capital to Nanjing. After the Qing general Yuan Shikai forced the abdication of the last Qing emperor and ensured the success of the revolution, the revolutionaries accepted him as president of the new Republic of China. Yuan maintained his capital at Beijing and quickly consolidated power, declaring himself emperor in 1915. His death less than a year later left China under the control of the warlords commanding the regional armies. Following the success of the Nationalists’ Northern Expedition, the capital was formally removed to Nanjing in 1928. On 28 June the same year, Beijing’s name was returned to Beiping (written at the time as “Peiping”).
During the Second Sino-Japanese War, Beiping fell to Japan on 29 July 1937 and was made the seat of the Provisional Government of the Republic of China, a puppet state that ruled the ethnic-Chinese portions of Japanese-occupied northern China. This government was later merged into the larger Wang Jingwei government based in Nanjing.
2.6 | People’s Republic of China
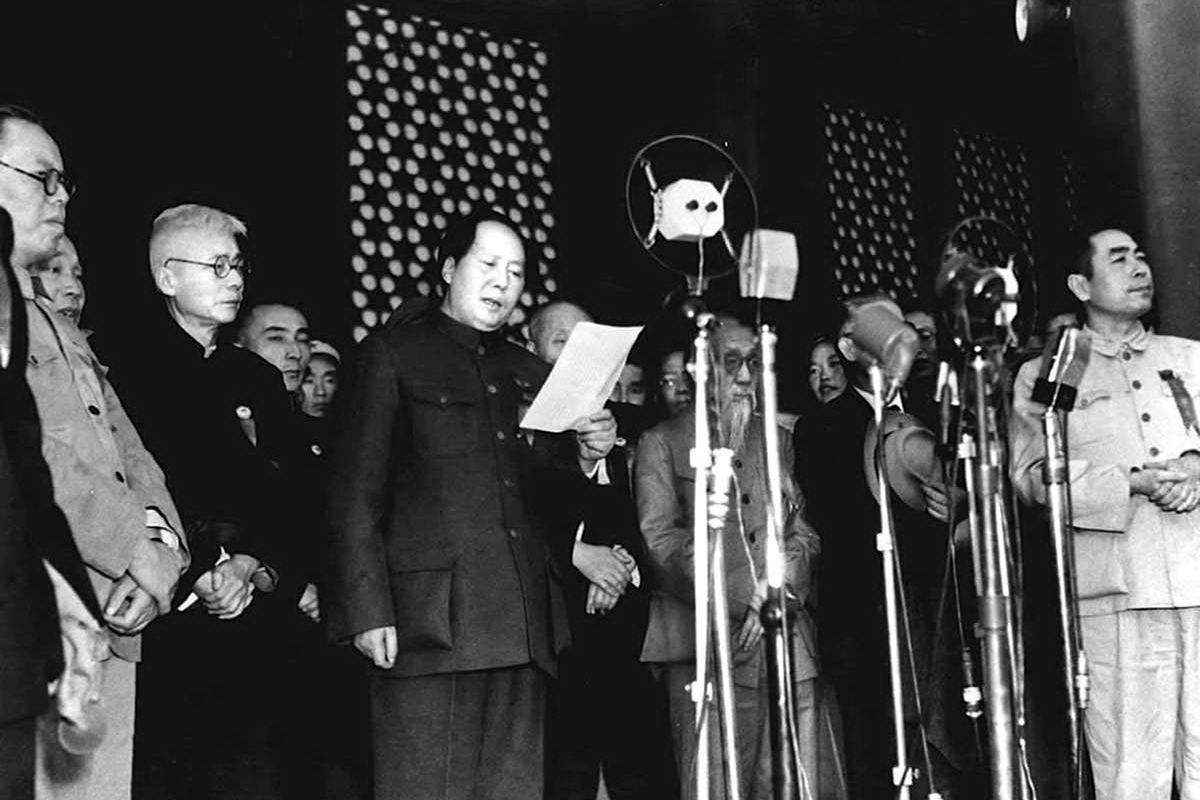

Mao Zedong proclaiming the establishment of the People’s Republic of China in 1949
In the final phases of the Chinese Civil War, the People’s Liberation Army seized control of the city peacefully on 31 January 1949 in the course of the Pingjin Campaign. On 1 October that year, Mao Zedong announced the creation of the People’s Republic of China from atop Tian’anmen. He restored the name of the city, as the new capital, to Beijing, a decision that had been reached by the Chinese People’s Political Consultative Conference just a few days earlier.
In the 1950s, the city began to expand beyond the old walled city and its surrounding neighborhoods, with heavy industries in the west and residential neighborhoods in the north. Many areas of the Beijing city wall were torn down in the 1960s to make way for the construction of the Beijing Subway and the 2nd Ring Road.
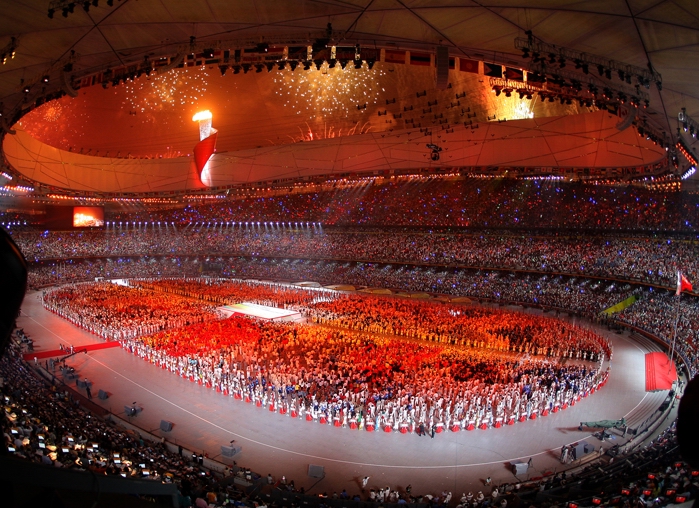

A scene from the opening ceremonies of the 2008 Summer Olympic Games.
During the Cultural Revolution from 1966 to 1976, the Red Guard movement began in Beijing and the city’s government fell victim to one of the first purges. By the fall of 1966, all city schools were shut down and over a million Red Guards from across the country gathered in Beijing for eight rallies in Tian’anmen Square with Mao. In April 1976, a large public gathering of Beijing residents against the Gang of Four and the Cultural Revolution in Tiananmen Square was forcefully suppressed. In October 1976, the Gang was arrested in Zhongnanhai and the Cultural Revolution came to an end. In December 1978, the Third Plenum of the 11th Party Congress in Beijing under the leadership of Deng Xiaoping reversed the verdicts against victims of the Cultural Revolution and instituted the “policy of reform and opening up.”
Since the early 1980s, the urban area of Beijing has expanded greatly with the completion of the 2nd Ring Road in 1981 and the subsequent addition of the 3rd, 4th, 5th and 6th Ring Roads. According to one 2005 newspaper report, the size of newly developed Beijing was one-and-a-half times larger than before. Wangfujing and Xidan have developed into flourishing shopping districts, while Zhongguancun has become a major center of electronics in China. In recent years, the expansion of Beijing has also brought to the forefront some problems of urbanization, such as heavy traffic, poor air quality, the loss of historic neighborhoods, and a significant influx of migrant workers from less-developed rural areas of the country. Beijing has also been the location of many significant events in recent Chinese history, principally the Tiananmen Square protests of 1989. The city has also hosted major international events, including the 2008 Summer Olympics and the 2015 World Championships in Athletics.
3 | Geography
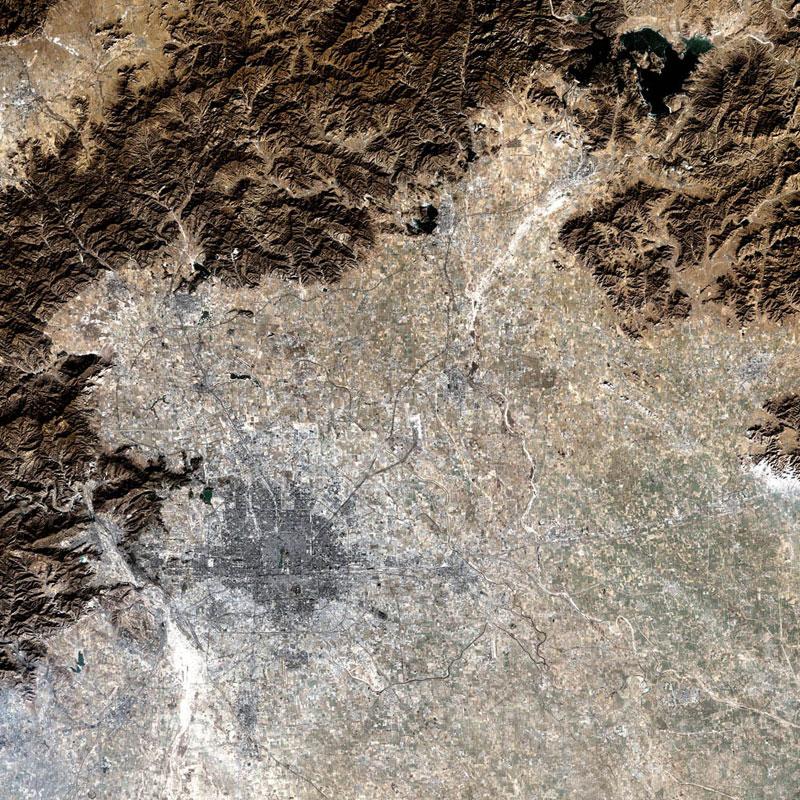

Landsat 7 Satellite image of Beijing Municipality with the surrounding mountains in dark brown
Beijing is situated at the northern tip of the roughly triangular North China Plain, which opens to the south and east of the city. Mountains to the north, northwest and west shield the city and northern China’s agricultural heartland from the encroaching desert steppes. The northwestern part of the municipality, especially Yanqing County and Huairou District, are dominated by the Jundu Mountains, while the western part is framed by Xishan or the Western Hills. The Great Wall of China across the northern part of Beijing Municipality was built on the rugged topography to defend against nomadic incursions from the steppes. Mount Dongling, in the Western Hills and on the border with Hebei, is the municipality’s highest point, with an altitude of 2,303 metres (7,556 ft).
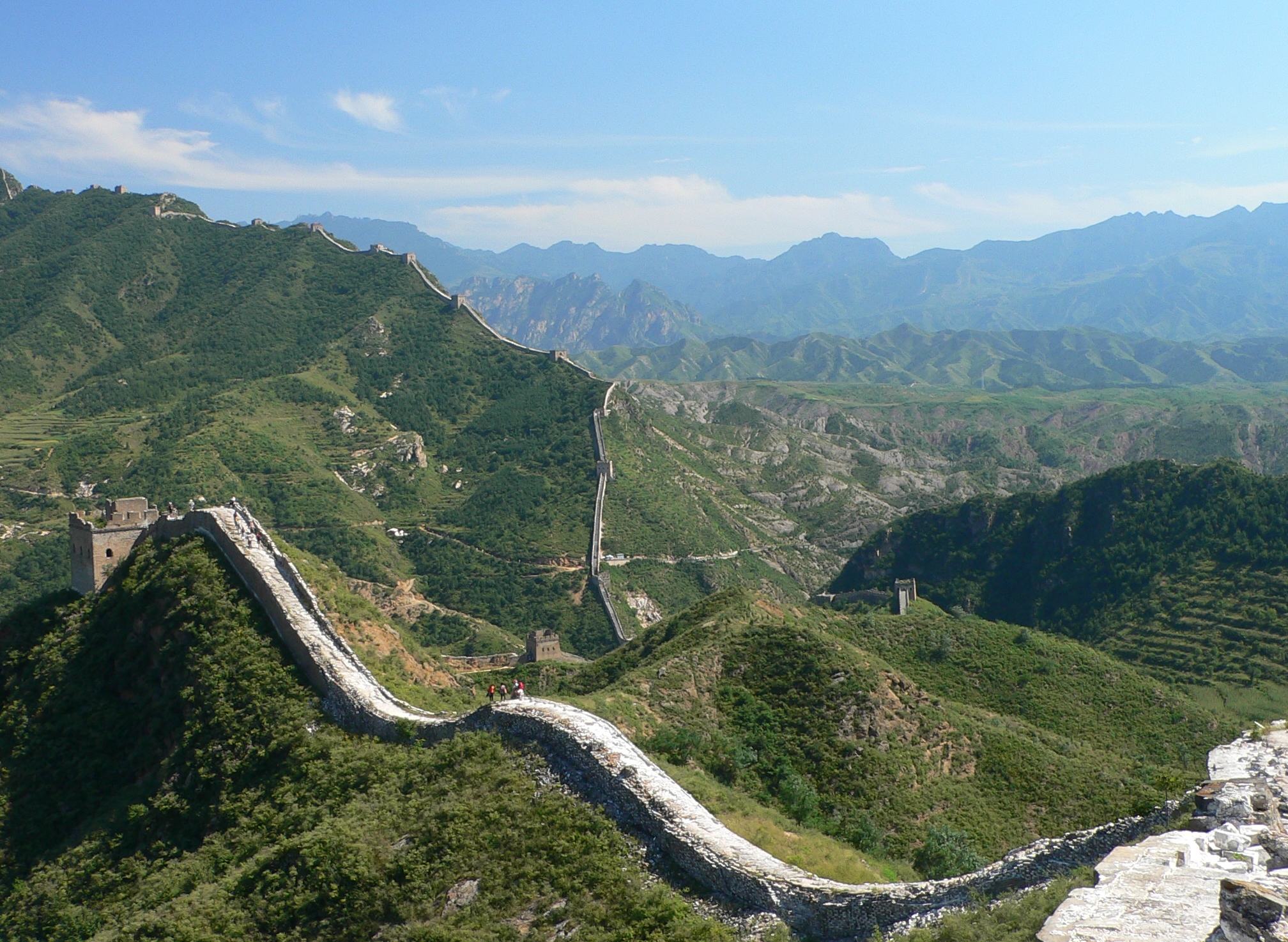

Remnants of the Great Wall of China in the mountains north of the city.
Major rivers flowing through the municipality, including the Chaobai, Yongding, Juma, are all tributaries in the Hai River system, and flow in a southeasterly direction. The Miyun Reservoir, on the upper reaches of the Chaobai River, is the largest reservoir within the municipality. Beijing is also the northern terminus of the Grand Canal to Hangzhou, which was built over 1,400 years ago as a transportation route, and the South–North Water Transfer Project, constructed in the past decade to bring water from the Yangtze River basin.
The urban area of Beijing, on the plains in the south-central of the municipality with elevation of 40 to 60 metres (130–200 feet), occupies a relatively small but expanding portion of the municipality’s area. The city spreads out in concentric ring roads. The Second Ring Road traces the old city walls and the Sixth Ring Road connects satellite towns in the surrounding suburbs. Tian’anmen and Tian’anmen Square are at the center of Beijing, directly to the south of the Forbidden City, the former residence of the emperors of China. To the west of Tian’anmen is Zhongnanhai, the residence of China’s current leaders. Chang’an Avenue, which cuts between Tiananmen and the Square, forms the city’s main east-west axis.
3.1 | Climate
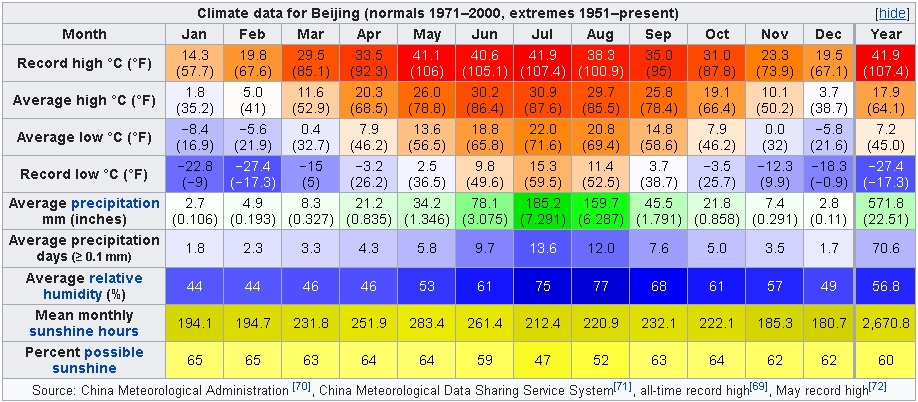
Beijing has a monsoon-influenced humid continental climate (Köppen climate classification Dwa), characterized by higher humidity in the summers due to the East Asian monsoon, and colder, windier, drier winters that reflect the influence of the vast Siberian anticyclone. Spring can bear witness to sandstorms blowing in from the Gobi Desert across the Mongolian steppe, accompanied by rapidly warming, but generally dry, conditions. Autumn, like Spring, is a season of transition and minimal precipitation. The monthly daily average temperature in January is −3.7 °C (25.3 °F), while in July it is 26.2 °C (79.2 °F). Precipitation averages around 570 mm (22 in) annually, with close to three-fourths of that total falling from June to August. With monthly percent possible sunshine ranging from 47% in July to 65% in January and February, the city receives 2,671 hours of bright sunshine annually. Extremes since 1951 have ranged from −27.4 °C (−17.3 °F) on 22 February 1966 to 41.9 °C (107.4 °F) on 24 July 1999 (unofficial record of 42.6 °C (108.7 °F) was set on 15 June 1942).
Climate data for Beijing (normals 1971–2000, extremes 1951–present)
3.2 | Environmental Problems
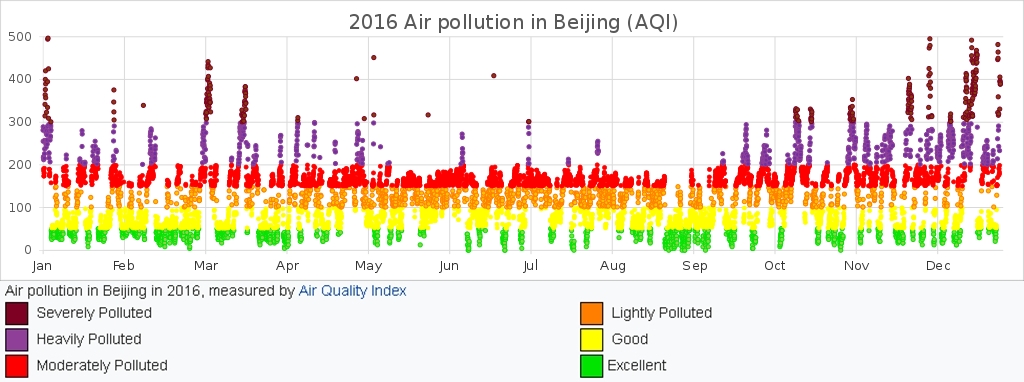
Beijing has a long history of environmental problems. Between 2000 and 2009 Beijing’s urban extent quadrupled, which not only strongly increased the extent of anthropogenic emissions, but also changed the meteorological situation fundamentally, even if emissions of human society are not included. For example, surface albedo, wind speed and humidity near the surface were decreased, whereas ground and near-surface air temperatures, vertical air dilution and ozone levels were increased. Because of the combined factors of urbanization and pollution caused by burning of fossil fuel, Beijing is often affected by serious environmental problems, which lead to health issues of many inhabitants. In 2013 heavy smog struck Beijing and most parts of northern China, in total 600 million people. After this “pollution shock” air pollution became an important economic and social concern in China. After that the government of Beijing announced measures to reduce air pollution, for example by lowering the share of coal from 24% in 2012 to 10% in 2017, while the national government ordered heavily polluting vehicles to be removed from 2015 to 2017 and increased its efforts to transition the energy system to clean sources.
Air Quality
Joint research between American and Chinese researchers in 2006 concluded that much of the city’s pollution comes from surrounding cities and provinces. On average 35–60% of the ozone can be traced to sources outside the city. Shandong Province and Tianjin Municipality have a “significant influence on Beijing’s air quality”, partly due to the prevailing south/southeasterly flow during the summer and the mountains to the north and northwest.

Heavy air pollution has resulted in widespread smog. These photographs, taken in August 2005, show the variations in Beijing’s air quality.
In preparation for the 2008 Summer Olympics and to fulfill promises to clean up the city’s air, nearly 17 billion USD was spent. Beijing implemented a number of air improvement schemes for the duration of the Games, including halting work at all construction sites, closing many factories in Beijing permanently, temporarily shutting industry in neighbouring regions, closing some gas stations, and cutting motor traffic by half by limiting drivers to odd or even days (based on their license plate numbers), reducing bus and subway fares, opening new subway lines, and banning high-emission vehicles. The city further assembled 3,800 natural gas-powered buses, one of the largest fleets in the world. Beijing became the first city in China to require the Chinese equivalent to the Euro 4 emission standard.
Coal burning accounts for about 40% of the PM 2.5 in Beijing and is also the chief source of nitrogen and sulphur dioxide. Since 2012, the city has been converting coal-fired power stations to burn natural gas and aims to cap annual coal consumption at 20 million tons. In 2011, the city burned 26.3 million tons of coal, 73% of which for heating and power generation and the remainder for industry. Much of the city’s air pollutants are emitted by neighbouring regions. Coal consumption in neighbouring Tianjin is expected to increase from 48 to 63 million tons from 2011 to 2015. Hebei Province burned over 300 million tons of coal in 2011, more than all of Germany, of which only 30% were used for power generation and a considerable portion for steel and cement making. Power plants in the coal-mining regions of Shanxi, Inner Mongolia and Shaanxi, where coal consumption has tripled since 2000, and Shandong also contribute to air pollution in Beijing. Shandong, Shanxi, Hebei and Inner Mongolia, respectively rank from first to fourth, among Chinese provinces by coal consumption. There were four major coal-fired power plants in the city to provide electricity as well as heating during the winter. The first one (Gaojing Thermal Power Plant) was shut down in 2014. Another two were shut in March 2015. The last one (Huaneng Thermal Power Plant) would be shut in 2016. Between 2013 and 2017, the city planned to reduce 13 million tons of coal consumption and cap coal consumption to 15 million tons in 2015.
The government sometimes uses cloud-seeding measures to increase the likelihood of rain showers in the region to clear the air prior to large events, such as prior to the 60th anniversary parade in 2009 as well as to combat drought conditions in the area. More recently, however, the government has increased its usage of such measures as closing factories temporarily and implementing greater restrictions for cars on the road, as in the case of “APEC blue” and “parade blue,” short periods during and immediately preceding the APEC China 2014 and the 2015 China Victory Day Parade, respectively. During and prior to these events, Beijing’s air quality improved dramatically, only to fall back to unhealthy levels shortly after.
Beijing air quality is often poor, especially in winter. In mid-January 2013, Beijing’s air quality was measured on top of the city’s US embassy at a PM2.5 density of 755 micrograms per cubic meter, which went off the US Environmental Protection Agency’s air quality index. It was widely reported, originally through a Twitter account, that the category was “crazy bad”. This was later changed to “beyond index”.
On 8 and 9 December 2015 Beijing had its first smog alert which shut down a majority of the industry and other commercial businesses in the city. Later in the month another smog “red alert” was issued.
According to Beijing’s environmental protection bureau’s announcement in November 2016, starting from 2017 highly polluting old cars wil be banned from being driven whenever Smog “red alerts” are issued in the city or neighboring regions.
Readings
Due to Beijing’s high-level of air pollution, there are various readings by different sources on the subject. Daily pollution readings at 27 monitoring stations around the city are reported on the website of the Beijing Environmental Protection Bureau (BJEPB). The American Embassy of Beijing also reports hourly fine particulate (PM2.5) and ozone levels on Twitter. Since the BJEPB and US Embassy measure different pollutants according to different criteria, the pollution levels and the impact to human health reported by the BJEPB are often lower than that reported by the US Embassy.
Air pollution in Beijing in 2016, measured by Air Quality Index
Dust from the erosion of deserts in northern and northwestern China results in seasonal dust storms that plague the city; the Beijing Weather Modification Office sometimes artificially induces rainfall to fight such storms and mitigate their effects. In the first four months of 2006 alone, there were no fewer than eight such storms. In April 2002, one dust storm alone dumped nearly 50,000 tons of dust onto the city before moving on to Japan and Korea.
4 | Politics and Government
Municipal government is regulated by the local Communist Party of China (CPC), led by the Beijing CPC Secretary (Chinese: 北京市委书记). The local CPC issues administrative orders, collects taxes, manages the economy, and directs a standing committee of the Municipal People’s Congress in making policy decisions and overseeing the local government.
Government officials include the mayor (Chinese: 市长) and vice-mayor. Numerous bureaus focus on law, public security, and other affairs. Additionally, as the capital of China, Beijing houses all of the important national governmental and political institutions, including the National People’s Congress.
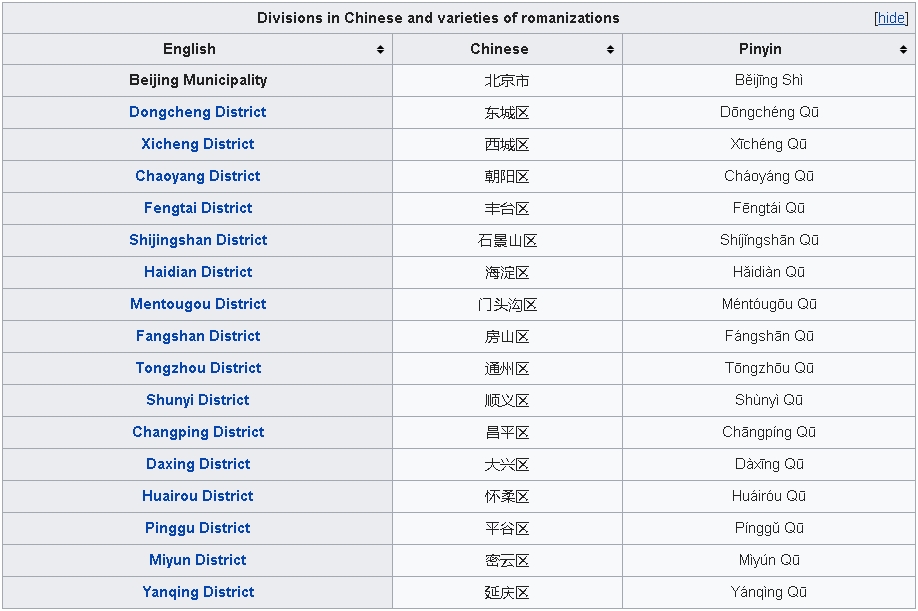
4.1 | Administrative Divisions
Beijing Municipality currently comprises 16 administrative county-level subdivisions including 16 urban, suburban, and rural districts. On 1 July 2010, Chongwen and Xuanwu were merged into Dongcheng and Xicheng, respectively. On 13 November 2015 Miyun and Yanqing were upgraded to districts.
Administrative Divisions of Beijing
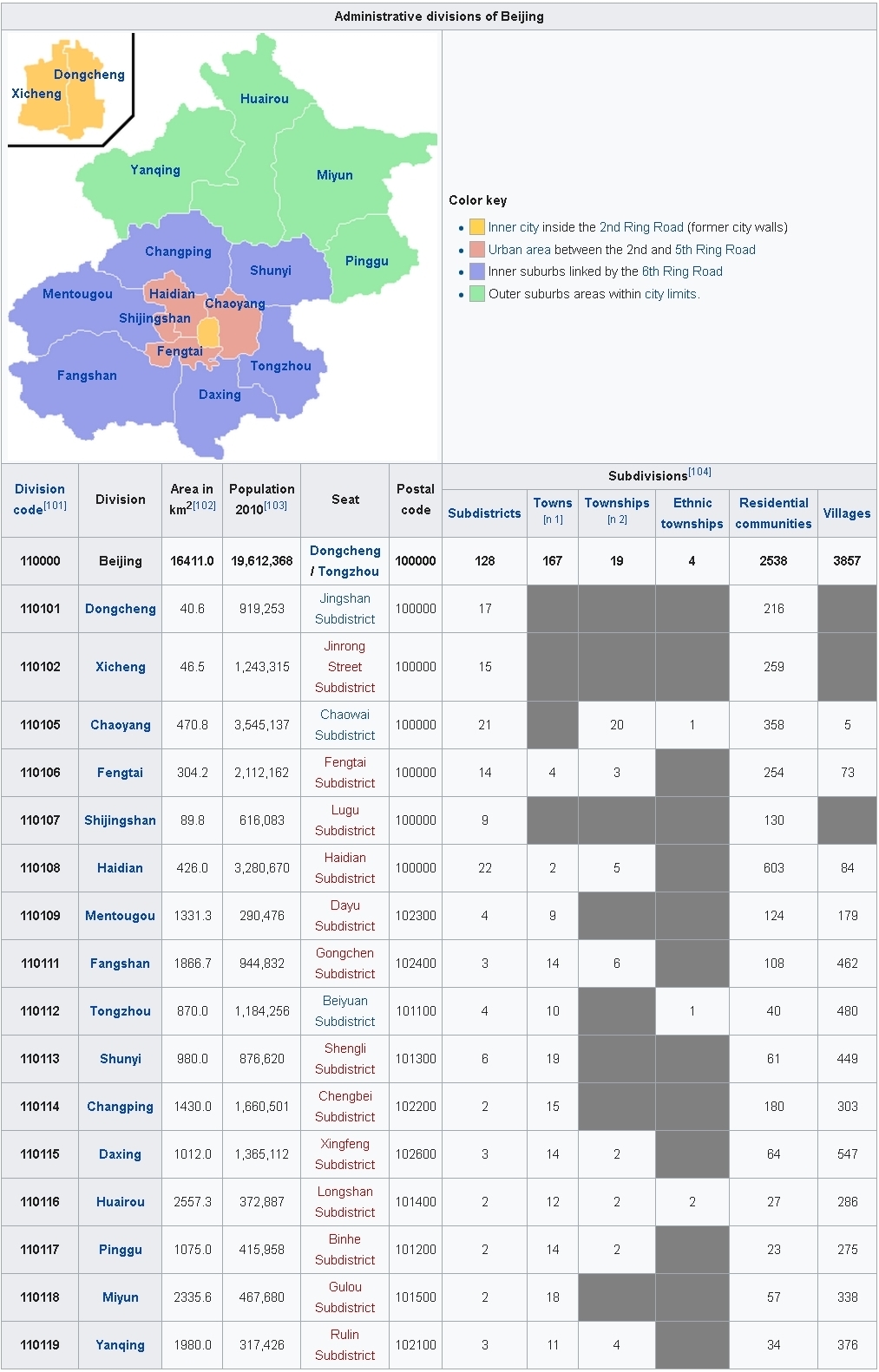
Divisions in Chinese and varieties of romanizations
- Jump up ^ Including “area” (地区).
- Jump up ^ Including other township related subdivisions.
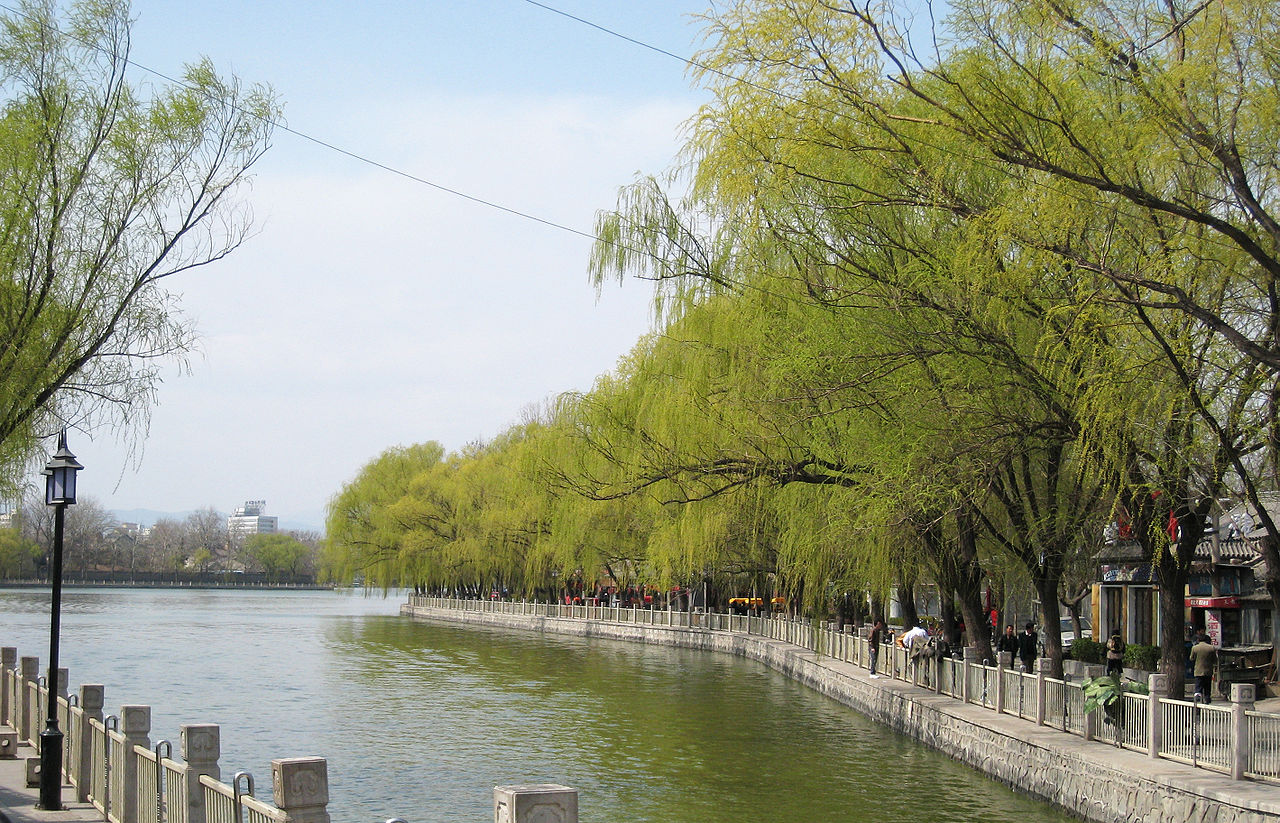

Shichahai, in the Xicheng District, is traditionally considered one of Beijing’s most beautiful and charming scenic areas.
Towns
Beijing’s 16 county-level divisions (districts) are further subdivided into 273 lower third-level administrative units at the township level: 119 towns, 24 townships, 5 ethnic townships and 125 subdistricts. Towns within Beijing Municipality but outside the urban area include (but are not limited to):
- Changping 昌平
- Huairou 怀柔
- Miyun 密云
- Liangxiang 良乡
- Liulimiao 琉璃庙
- Tongzhou 通州
- Yizhuang 亦庄
- Tiantongyuan 天通苑
- Beiyuan 北苑
- Xiaotangshan 小汤山
Several place names in Beijing end with mén (门), meaning “gate”, as they were the locations of gates in the former Beijing city wall. Other place names end in cūn (村), meaning “village”, as they were originally villages outside the city wall.
Neighborhoods
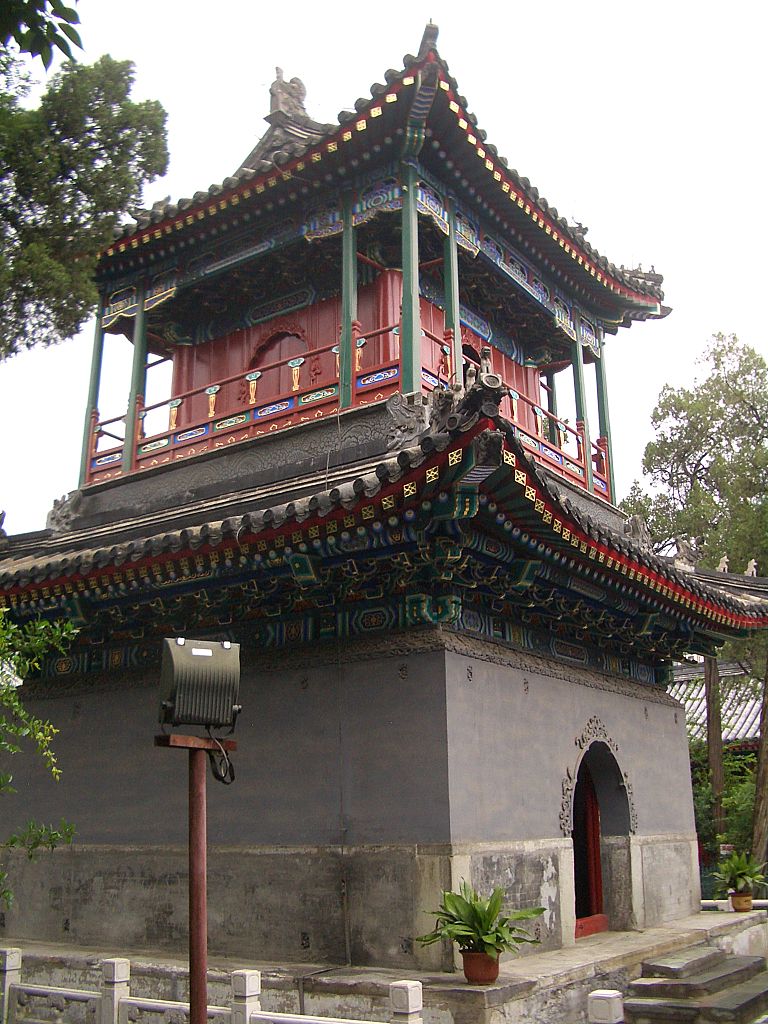

The Niujie Mosque is an important historical attraction
Neighborhoods may extend across multiple districts. Major neighborhoods in urban Beijing include:
- Qianmen 前门
- Tian’anmen 天安门
- Di’anmen 地安门
- Chongwenmen 崇文门
- Xuanwumen 宣武门
- Fuchengmen 阜成门
- Xizhimen 西直门
- Deshengmen 德胜门
- Andingmen 安定门
- Sanlitun 三里屯
- Dongzhimen 东直门
- Chaoyangmen 朝阳门
- Yongdingmen 永定门
- Zuo’anmen 左安门
- You’anmen 右安门
- Guangqumen 广渠门
- Guang’anmen 广安门
- Huashi 花市
- Xibianmen 西便门
- Hepingmen 和平门
- Fuxingmen 复兴门
- Jianguomen 建国门
- Gongzhufen 公主坟
- Fangzhuang 方庄
- Guomao 国贸
- Hepingli 和平里
- Ping’anli 平安里
- Beixinqiao 北新桥
- Jiaodaokou 交道口
- Kuanjie 宽街
- Wangjing 望京
- Wangfujing 王府井
- Dengshikou 灯市口
- Wudaokou 五道口
- Xidan 西单
- Dongdan 东单
- Zhongguancun 中关村
- Panjiayuan 潘家园
- Beijing CBD 北京商务中心区
- Yayuncun 亚运村
- Shifoying 石佛营
4.2| Judiciary and procuracy
The judicial system in Beijing consists of the Supreme People’s Court, the highest court in the country, the Beijing Municipal High People’s Court, the high people’s court of the municipality, three intermediate people’s courts, one intermediate railway transport court, 14 basic people’s court (one for each of the municipality’s districts and counties), and one basic railway transport court. The Beijing No. 1 Intermediate People’s Court in Shijingshan oversees the basic courts of Haidian, Shijingshan, Mentougou, Changping and Yanqing. The Beijing No. 2 Intermediate People’s Court in Fengtai oversees the basic courts of Dongcheng, Xicheng, Fengtai, Fangshan and Daxing. The Beijing No. 3 Intermediate People’s Court in Laiguangying, is the newest of the three intermediate people’s courts and opened on 21 August 2013. It oversees the district courts of Chaoyang, Tongzhou, Shunyi, Huairou, Pinggu and Miyun. Each court in Beijing has a corresponding people’s procuratorate.
4.3 | Diplomatic Missions
About 163 countries have embassies in Beijing, which are concentrated in Jianguomenwai, Sanlitun and Liangmaqiao in Chaoyang District.
5 | Economy
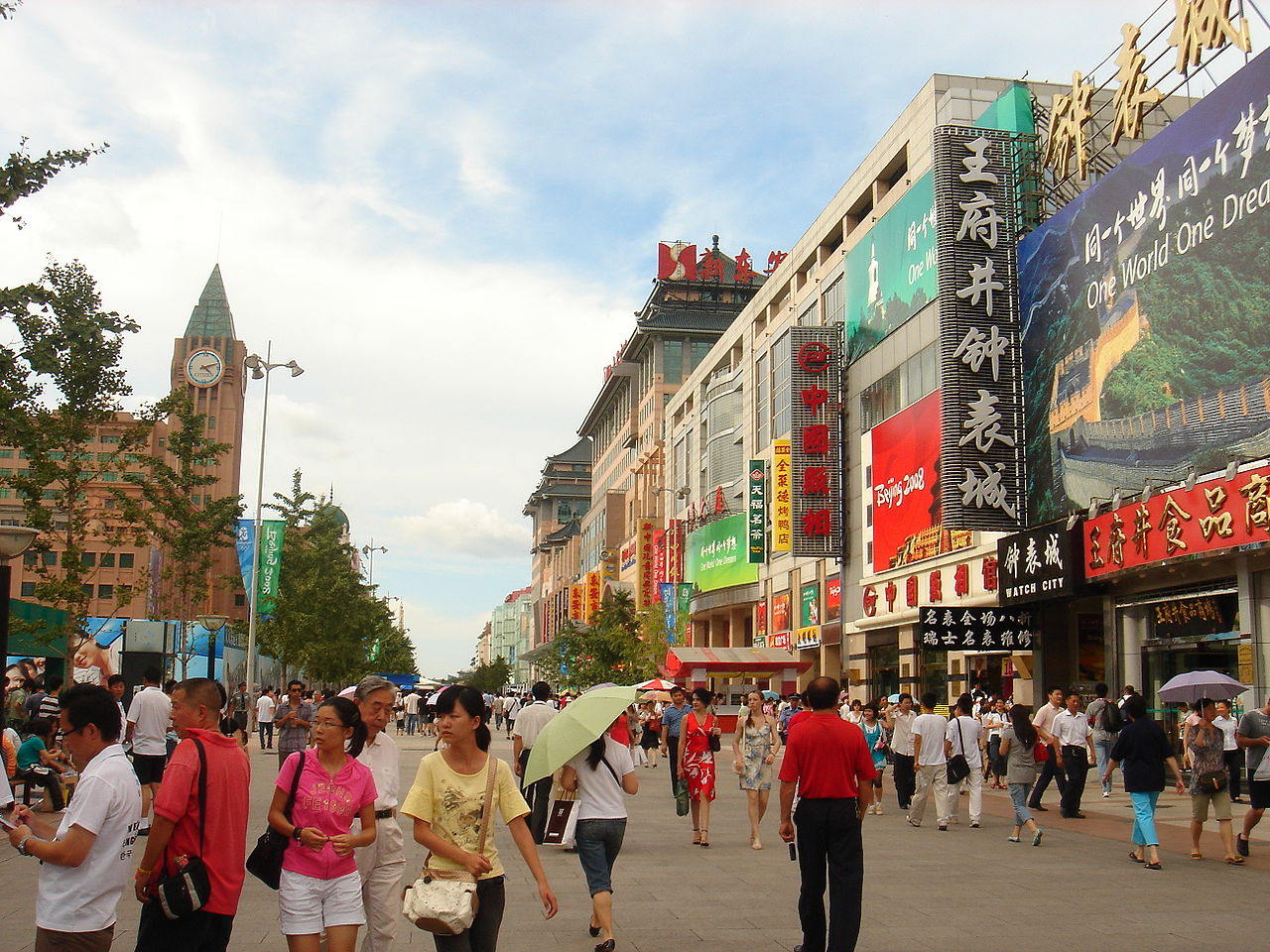

Wangfujing Street is one of the oldest and busiest shopping streets in Beijing with nearly 100,000 visitors daily (August 2008). The sale of consumer goods both retail and wholesale accounted for about ⅛ of Beijing’s economic output in 2013.
Beijing’s economy ranks among the most developed and prosperous in China. In 2013, the municipality’s nominal gross domestic product (GDP) was CN¥1.95 trillion (US$314 billion), about 3.43% of the country’s total output, and ranked 13th among province-level administrative units. Per capita GDP, at CN¥93,213 (US$15,051) in nominal terms and Int$21,948 at purchasing power parity, was 2.2 times the national average and ranked second among province-level administrative units. The economy tripled in size from 2004 to 2012, and grew at an annual rate of 7.7% in 2013.
Due to the concentration of state owned enterprises in the national capital, Beijing in 2013 had more Fortune Global 500 Company headquarters than any other city in the world.
5.1 | Sector Composition
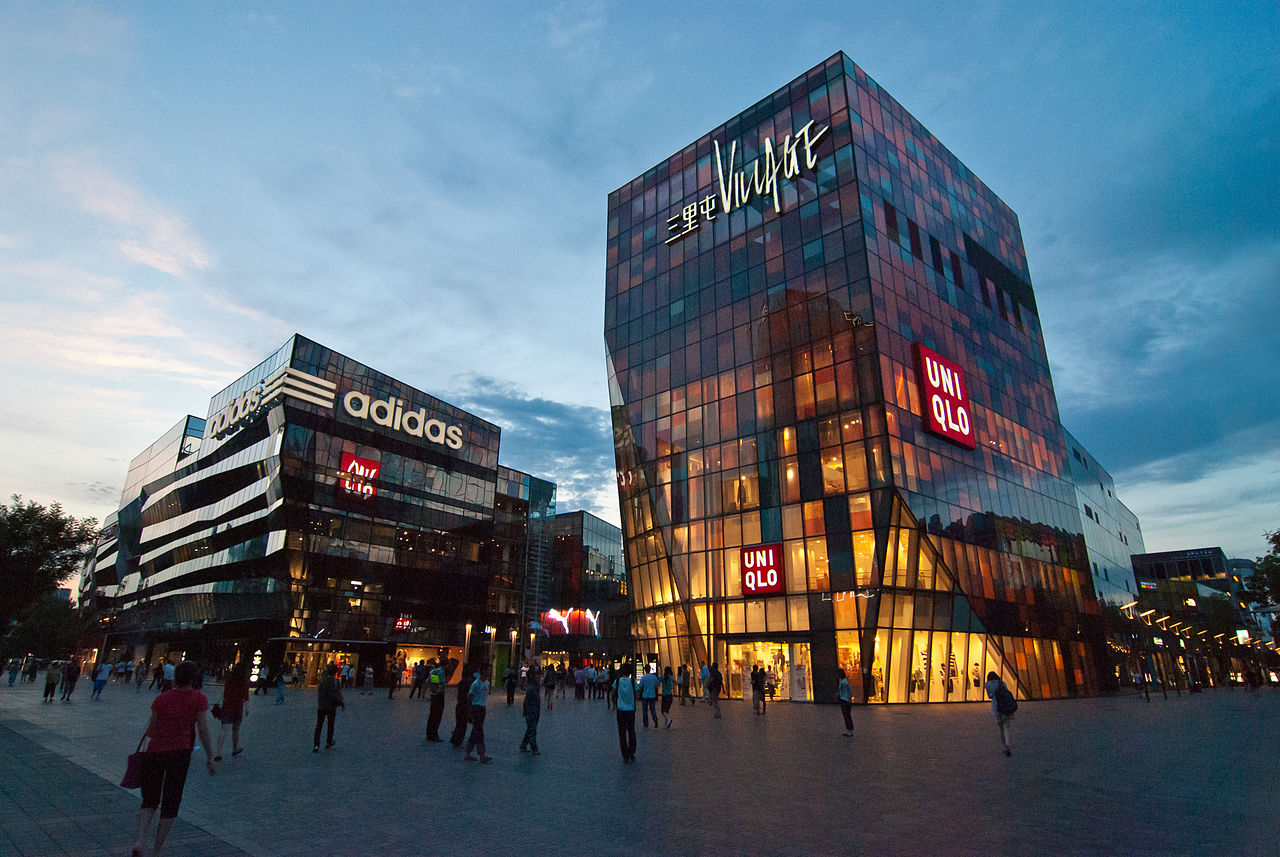

The Taikoo Li Sanlitun shopping arcade is a popular destination among locals and visitors
The city has a post-industrial economy that is dominated by the tertiary sector (services), which generated 76.9% of output, followed by the secondary sector (manufacturing, construction) at 22.2% and the primary sector (agriculture, mining) at 0.8%.
The services sector is broadly diversified with professional services, wholesale and retail, information technology, commercial real estate, scientific research, and residential real estate each contributing at least 6% to the city’s economy in 2013.
The single largest sub-sector remains industry, whose share of overall output has shrunk to 18.1% in 2013. The mix of industrial output has changed significantly since 2010 when the city announced that 140 highly-polluting, energy and water resource intensive enterprises would be relocated from the city in five years. The relocation of Capital Steel to neighbouring Hebei province had begun in 2005. In 2013, output of automobiles, aerospace products, semiconductors, pharmaceuticals, and food processing all increased.
In the farmland around Beijing, vegetables and fruits have displaced grain as the primary crops under cultivation. In 2013, the tonnage of vegetable, edible fungus and fruit harvested was over three times that of grain. In 2013, overall acreage under cultivation shrank along with most categories of produce as more land was reforested for environmental reasons.
5.2 | Economic Zones
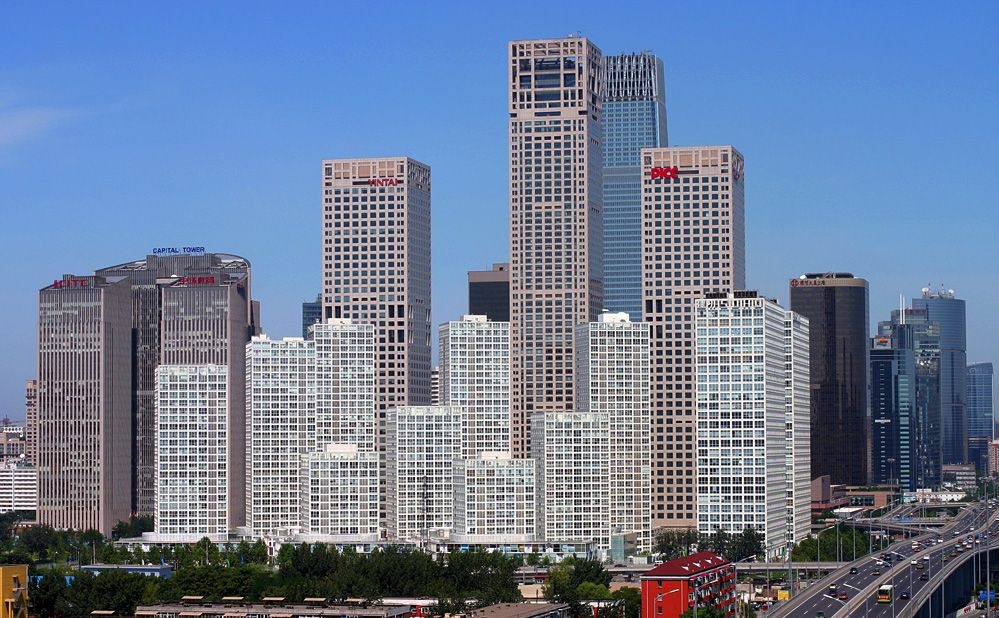

Beijing CBD

Zhongguancun is a technology hub in Haidian District
In 2006, the city government identified six high-end economic output zones around Beijing as the primary engines for local economic growth. In 2012, the six zones produced 43.3% of the city’s GDP, up from 36.5% in 2007. The six zones are:
- Zhongguancun, China’s silicon village in Haidian District northwest of the city, is home to both established and start-up tech companies. As of the second quarter of 2014, of the 9,895 companies registered in one of the six zones, 6,150 were based in Zhongguancun.
- Beijing Financial Street, in Xicheng District on the west side of the city between Fuxingmen and Fuchengmen, is lined with headquarters of large state banks and insurance companies. The country’s financial regulatory agencies including the central bank, bank regulator, securities regulator, and foreign exchange authority are located in the neighborhood.
- Beijing Central Business District (CBD), is actually located to the east of downtown, near the embassies along the eastern Third Ring Road between Jianguomenwai and Chaoyangmenwai. The CBD is home to most of the city’s skyscraper office buildings. Most of the city’s foreign companies and professional service firms are based in the CBD.
- Beijing Economic and Technological Development Area, better known as Yizhuang, is an industrial park the straddles the southern Fifth Ring Road in Daxing District. It has attracted pharmaceutical, information technology, and materials engineering companies.
- Beijing Airport Economic Zone was created in 1993 and surrounds the Beijing Capital International Airport in Shunyi District northwest of the city. In addition to logistics, airline services, and trading firms, this zone is also home to Beijing’s automobile assembly plants.
- Beijing Olympic Center Zone surrounds the Olympic Green due north of downtown and is developing into an entertainment, sports, tourism and business convention center.
Shijingshan, on the western outskirts of the city, is a traditional heavy industrial base for steel-making. Chemical plants are concentrated in the far eastern suburbs.
Less legitimate enterprises also exist. Urban Beijing is known for being a center of infringed goods; anything from the latest designer clothing to DVDs can be found in markets all over the city, often marketed to expatriates and international visitors.
6 | Demographics
Historical population
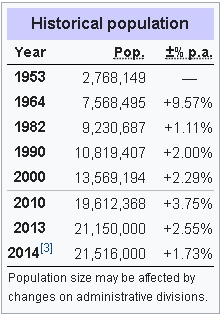
Population size may be affected by changes on administrative divisions.
In 2013, Beijing had a total population of 21.148 million within the municipality, of which 18.251 million resided in urban districts or suburban townships and 2.897 million lived in rural villages. Within China, the city ranked second in urban population after Shanghai and the third in municipal population after Shanghai and Chongqing. Beijing also ranks among the most populous cities in the world, a distinction the city has held for much of the past 800 years, especially during the 15th to early 19th centuries when it was the largest city in the world.
About 13 million of the city’s residents in 2013 had local hukou permits, which entitles them to permanent residence in Beijing. The remaining 8 million residents had hukou permits elsewhere and were not eligible to receive some social benefits provided by the Beijing municipal government.
The population increased in 2013 by 455,000 or about 7% from the previous year and continued a decade-long trend of rapid growth. The total population in 2004 was 14.213 million. The population gains are driven largely by migration. The population’s rate of natural increase in 2013 was a mere 0.441%, based on a birth rate of 8.93 and a mortality rate of 4.52. The gender balance was 51.6% males and 48.4% females.
Working age people account for nearly 80% of the population. Compared to 2004, residents age 0–14 as a proportion of the population dropped from 9.96% to 9.5% in 2013 and residents over the age of 65 declined from 11.12% to 9.2%.
According to the 2010 census, nearly 96% of Beijing’s population are ethnic Han Chinese. Of the 800,000 ethnic minorities living in the capital, Manchu (336,000), Hui (249,000), Korean (77,000), Mongol (37,000) and Tujia (24,000) constitute the five largest groups. In addition, there were 8,045 Hong Kong residents, 500 Macau residents, and 7,772 Taiwan residents along with 91,128 registered foreigners living in Beijing. A study by the Beijing Academy of Sciences estimates that in 2010 there were on average 200,000 foreigners living in Beijing on any given day including students, business travellers and tourists are not counted as registered residents.
From 2000 to 2010, the percentage of city residents with at least some college education nearly doubled from 16.8% to 31.5%. About 22.2% have some high school education and 31% had reached middle school.
7 | Culture

The Old Beijing Observatory
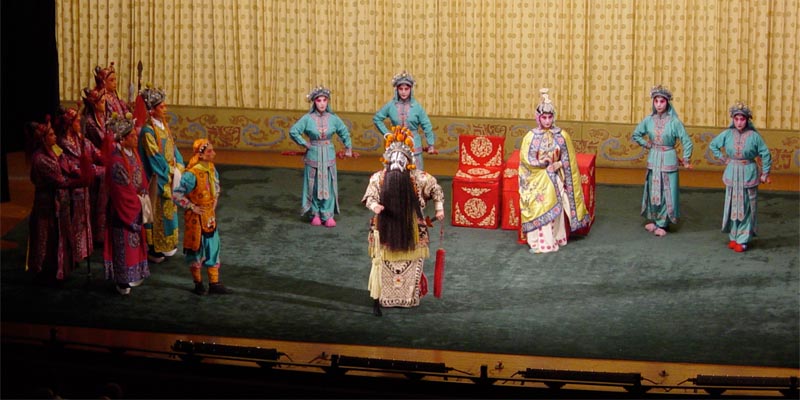

A scene from a Peking opera
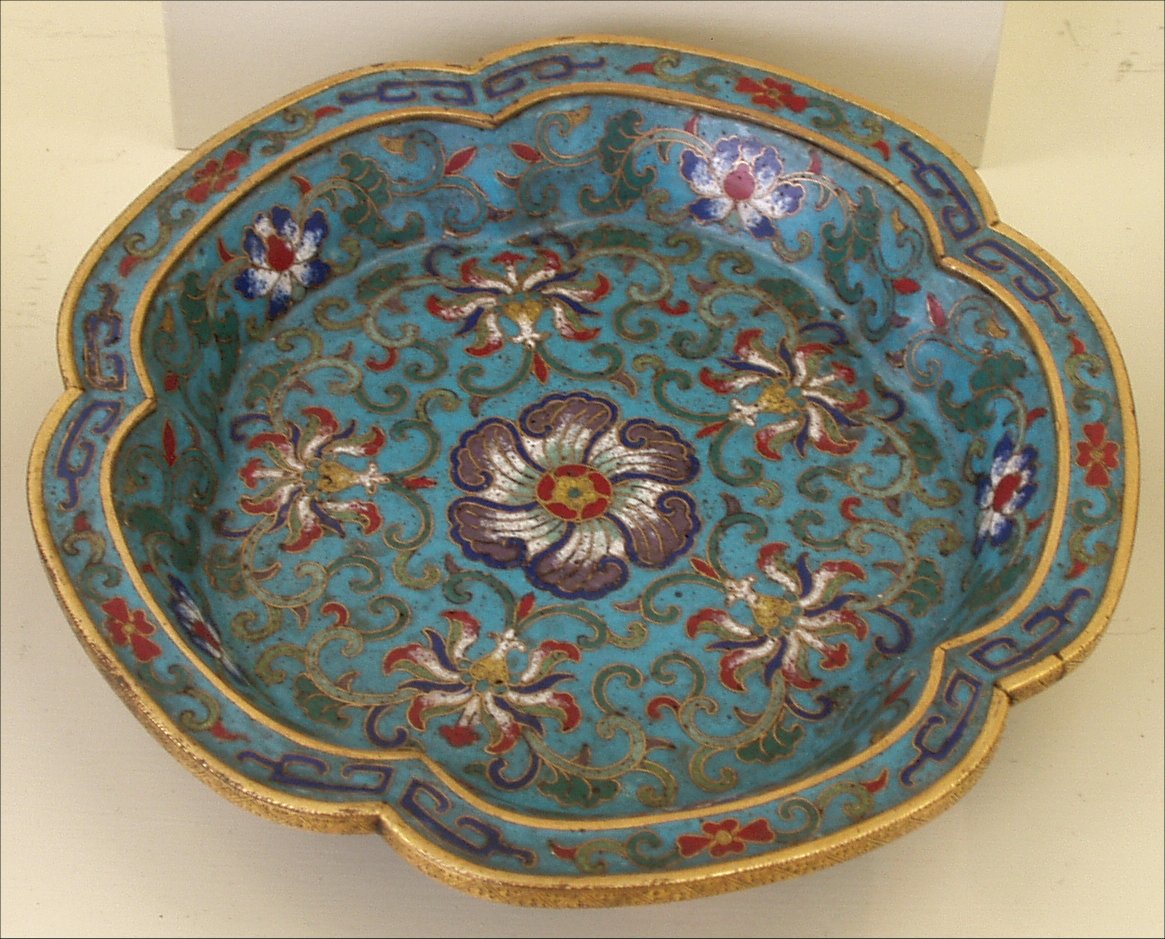

A Chinese cloisonné dish from the Qing dynasty
People native to urban Beijing speak the Beijing dialect, which belongs to the Mandarin subdivision of spoken Chinese. This speech is the basis for putonghua, the standard spoken language used in mainland China and Taiwan, and one of the four official languages of Singapore. Rural areas of Beijing Municipality have their own dialects akin to those of Hebei province, which surrounds Beijing Municipality.
Beijing or Peking opera (京剧, Jīngjù) is a traditional form of Chinese theater well known throughout the nation. Commonly lauded as one of the highest achievements of Chinese culture, Beijing opera is performed through a combination of song, spoken dialogue, and codified action sequences involving gestures, movement, fighting and acrobatics. Much of Beijing opera is carried out in an archaic stage dialect quite different from Modern Standard Chinese and from the modern Beijing dialect.
Beijing cuisine is the local style of cooking. Peking Roast Duck is perhaps the best known dish. Fuling Jiabing, a traditional Beijing snack food, is a pancake (bing) resembling a flat disk with a filling made from fu ling, a fungus used in traditional Chinese medicine. Teahouses are common in Beijing.
The cloisonné (or Jingtailan, literally “Blue of Jingtai”) metalworking technique and tradition is a Beijing art speciality, and is one of the most revered traditional crafts in China. Cloisonné making requires elaborate and complicated processes which include base-hammering, copper-strip inlay, soldering, enamel-filling, enamel-firing, surface polishing and gilding. Beijing’s lacquerware is also well known for its sophisticated and intrinsic patterns and images carved into its surface, and the various decoration techniques of lacquer include “carved lacquer” and “engraved gold”.
Younger residents of Beijing have become more attracted to the nightlife, which has flourished in recent decades, breaking prior cultural traditions that had practically restricted it to the upper class. Today, Houhai, Sanlitun and Wudaokou are Beijing’s nightlife hotspots.
7.1 | Places of interest
…the city remains an epicenter of tradition with the treasures of nearly 2,000 years as the imperial capital still on view—in the famed Forbidden City and in the city’s lush pavilions and gardens…
— National Geographic

Qianmen Avenue, a traditional commercial street in Beijing
At the historical heart of Beijing lies the Forbidden City, the enormous palace compound that was the home of the emperors of the Ming and Qing dynasties; the Forbidden City hosts the Palace Museum, which contains imperial collections of Chinese art. Surrounding the Forbidden City are several former imperial gardens, parks and scenic areas, notably Beihai, Shichahai, Zhongnanhai, Jingshan and Zhongshan. These places, particularly Beihai Park, are described as masterpieces of Chinese gardening art, and are popular tourist destinations with tremendous historical importance; in the modern era, Zhongnanhai has also been the political heart of various Chinese governments and regimes and is now the headquarters of the Communist Party of China and the State Council. From Tiananmen Square, right across from the Forbidden City, there are several notable sites, such as the Tiananmen, Qianmen, the Great Hall of the People, the National Museum of China, the Monument to the People’s Heroes, and the Mausoleum of Mao Zedong. The Summer Palace and the Old Summer Palace both lie at the western part of the city; the former, a UNESCO World Heritage Site, contains a comprehensive collection of imperial gardens and palaces that served as the summer retreats for the Qing imperial family.
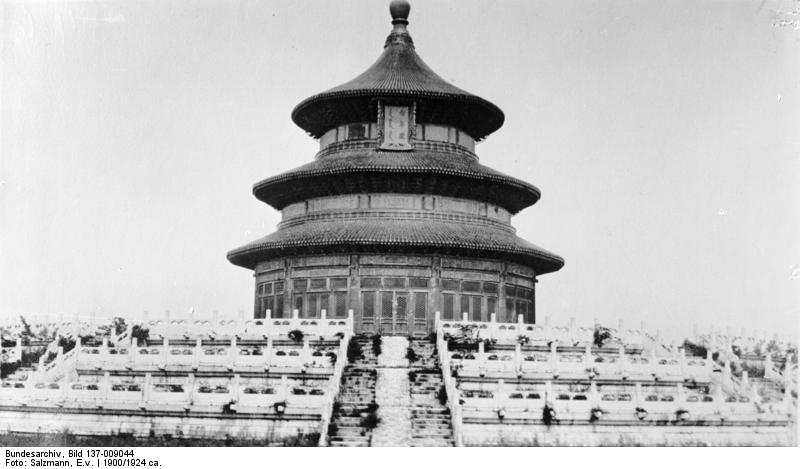

Beijing’s Temple of Heaven as photographed in the early 20th century
Among the best known religious sites in the city is the Temple of Heaven (Tiantan), located in southeastern Beijing, also a UNESCO World Heritage Site, where emperors of the Ming and Qing dynasties made visits for annual ceremonies of prayers to Heaven for good harvest. In the north of the city is the Temple of Earth (Ditan), while the Temple of the Sun (Ritan) and the Temple of the Moon (Yuetan) lie in the eastern and western urban areas respectively. Other well-known temple sites include the Dongyue Temple, Tanzhe Temple, Miaoying Temple, White Cloud Temple, Yonghe Temple, Fayuan Temple, Wanshou Temple and Big Bell Temple. The city also has its own Confucius Temple, and a Guozijian or Imperial Academy. The Cathedral of the Immaculate Conception, built in 1605, is the oldest Catholic church in Beijing. The Niujie Mosque is the oldest mosque in Beijing, with a history stretching back over a thousand years.
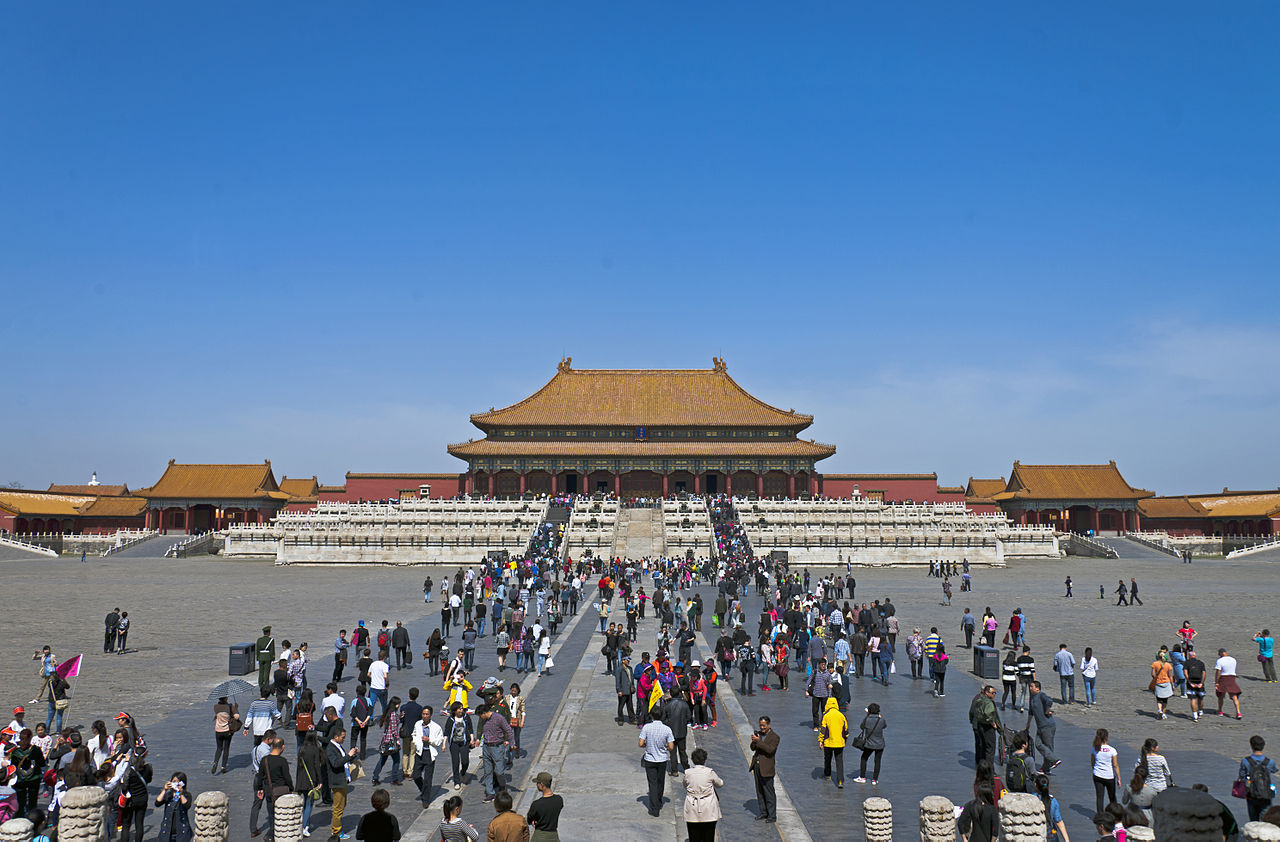

Inside the Forbidden City
Beijing contains several well-preserved pagodas and stone pagodas, such as the towering Pagoda of Tianning Temple, which was built during the Liao Dynasty from 1100 to 1120, and the Pagoda of Cishou Temple, which was built in 1576 during the Ming Dynasty. Historically noteworthy stone bridges include the 12th-century Lugou Bridge, the 17th-century Baliqiao bridge, and the 18th-century Jade Belt Bridge. The Beijing Ancient Observatory displays pre-telescopic spheres dating back to the Ming and Qing dynasties. The Fragrant Hills (Xiangshan) is a popular scenic public park that consists of natural landscaped areas as well as traditional and cultural relics. The Beijing Botanical Garden exhibits over 6,000 species of plants, including a variety of trees, bushes and flowers, and an extensive peony garden. The Taoranting, Longtan, Chaoyang, Haidian, Milu Yuan and Zizhu Yuan parks are some of the notable recreational parks in the city. The Beijing Zoo is a center of zoological research that also contains rare animals from various continents, including the Chinese giant panda.
There are 144 museums and galleries (as of June 2008) in the city. In addition to the Palace Museum in the Forbidden City and the National Museum of China, other major museums include the National Art Museum of China, the Capital Museum, the Beijing Art Museum, the Military Museum of the Chinese People’s Revolution, the Geological Museum of China, the Beijing Museum of Natural History and the Paleozoological Museum of China.
Located at the outskirts of urban Beijing, but within its municipality are the Thirteen Tombs of the Ming Dynasty, the lavish and elaborate burial sites of thirteen Ming emperors, which have been designated as part of the UNESCO World Heritage Site Imperial Tombs of the Ming and Qing Dynasties. The archaeological Peking Man site at Zhoukoudian is another World Heritage Site within the municipality, containing a wealth of discoveries, among them one of the first specimens of Homo erectus and an assemblage of bones of the gigantic hyena Pachycrocuta brevirostris. There are several sections of the UNESCO World Heritage Site Great Wall of China, most notably Badaling, Jinshanling, Simatai and Mutianyu.
7.2 | Architecture
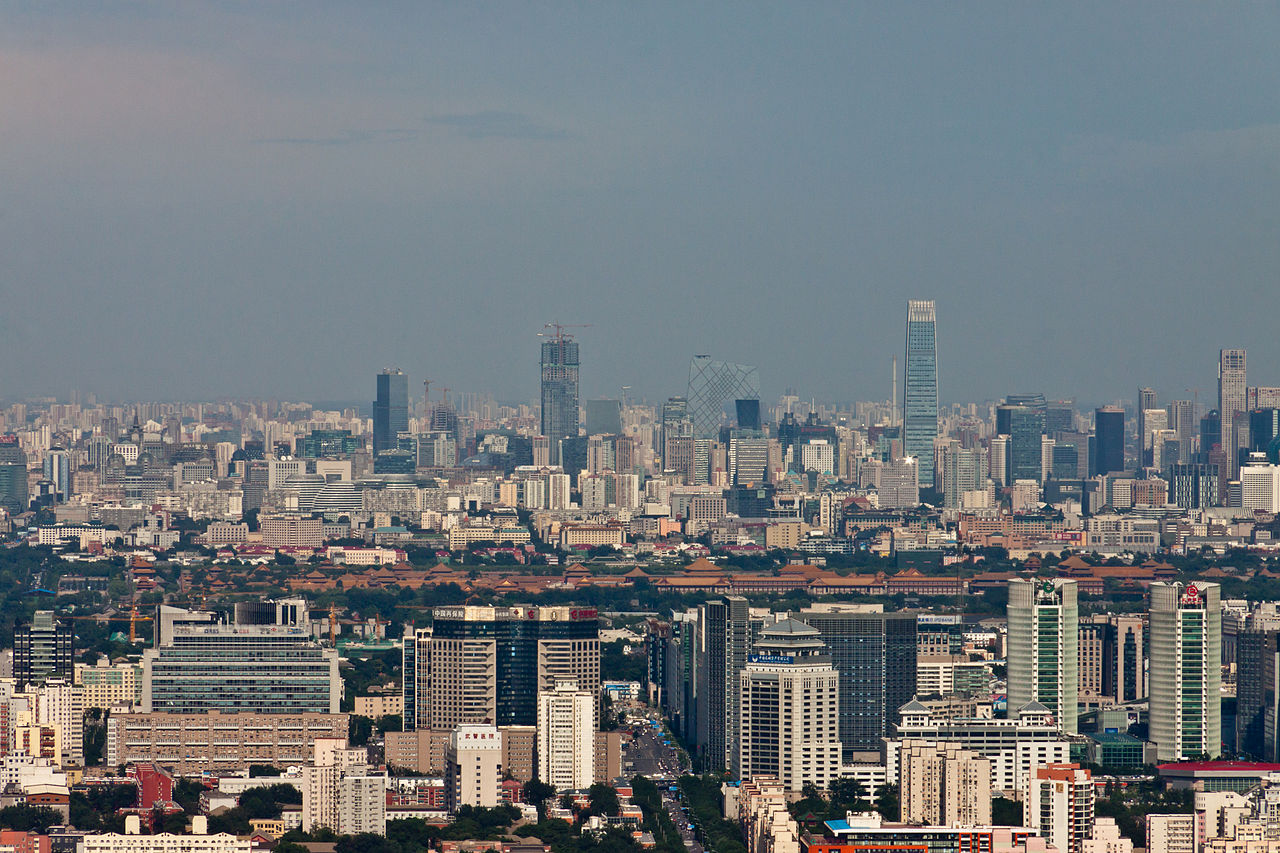

City Skyline
Three styles of architecture are predominant in urban Beijing. First, there is the traditional architecture of imperial China, perhaps best exemplified by the massive Tian’anmen (Gate of Heavenly Peace), which remains the People’s Republic of China’s trademark edifice, the Forbidden City, the Imperial Ancestral Temple and the Temple of Heaven. Next, there is what is sometimes referred to as the “Sino-Sov” style, with structures tending to be boxy and sometimes poorly constructed, which were built between the 1950s and the 1970s. Finally, there are much more modern architectural forms, most noticeably in the area of the Beijing CBD in east Beijing such as the new CCTV Headquarters, in addition to buildings in other locations around the city such as the Beijing National Stadium and National Center for the Performing Arts.
Since 2007, buildings in Beijing have received the CTBUH Skyscraper Award for best overall tall building twice, for the Linked Hybrid building in 2009 and the CCTV Headquarters in 2013. The CTBUH Skyscraper award for best tall overall building is given to only one building around the world every year.
In the early 21st century, Beijing has witnessed tremendous growth of new building constructions, exhibiting various modern styles from international designers, most pronounced in the CBD region. A mixture of both 1950s design and neofuturistic style of architecture can be seen at the 798 Art Zone, which mixes the old with the new. Beijing’s current completed tallest building is the 330-meter China World Trade Center Tower III, but will be surpassed by the 528-meter China Zun in 2018 when it is completed. Both buildings are in the Beijing CBD.
Beijing is famous for its siheyuans, a type of residence where a common courtyard is shared by the surrounding buildings. Among the more grand examples are the Prince Gong Mansion and Residence of Soong Ching-ling. These courtyards are usually connected by alleys called hutongs. The hutongs are generally straight and run east to west so that doorways face north and south for good Feng Shui. They vary in width; some are so narrow only a few pedestrians can pass through at a time. Once ubiquitous in Beijing, siheyuans and hutongs are rapidly disappearing, as entire city blocks of hutongs are replaced by high-rise buildings. Residents of the hutongs are entitled to live in the new buildings in apartments of at least the same size as their former residences. Many complain, however, that the traditional sense of community and street life of the hutongs cannot be replaced, and these properties are often government owned.
7.3 | Religion
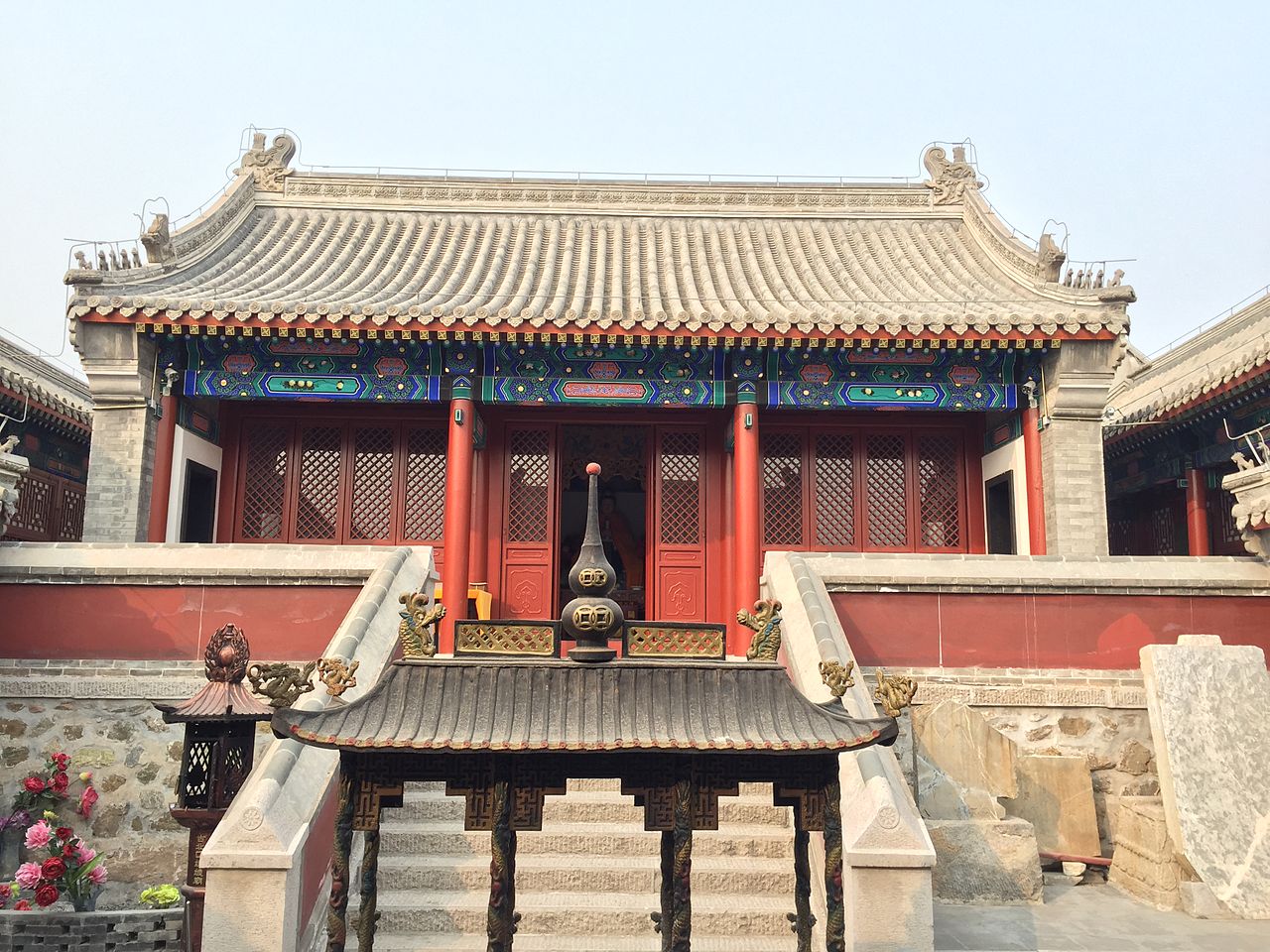

A Temple of the Goddess in Gubeikou.

Fire God Temple in Di’anmen.
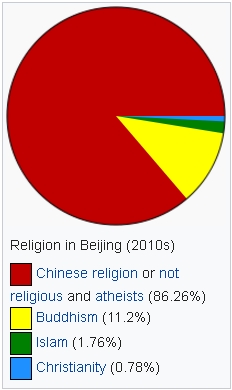
The religious heritage of Beijing is rich and diverse as Chinese folk religion, Taoism, Buddhism, Confucianism, Islam and Christianity all have significant historical presence in the city. As the national capital, the city also hosts the State Administration for Religious Affairs and various state-sponsored institutions of the leading religions. In recent decades, foreign residents have brought other religions to the city. According to Wang Zhiyun of the Chinese Academy of Social Sciences in 2010 there were 2.2 million Buddhists in the city, equal to 11.2% of the total population. According to the Chinese General Social Survey of 2009, Christians constitute 0.78% of the city’s population. According to a 2010 survey, Muslims constitute 1.76% of the population of Beijing.

Rear hall of the Capital City God Temple of Beijing.
Chinese Folk Religion and Taoism
Beijing has many temples dedicated to folk religious and communal deities, many of which are being reconstructed or refurbished in the 2000s and 2010s. Yearly sacrifices to the God of Heaven (祭天 jìtiān) at the Temple of Heaven have been resumed by Confucian groups in the 2010s.
There are temples dedicated to the worship of the Goddess (娘娘 Niángniáng) in the city, one of them near the Olympic Village, and they revolve around a major cult center at Mount Miaofeng. There are also many temples consecrated to the Dragon God (龙神 Lóngshén), to the Medicine Master (药王 Yàowáng), to Divus Guan (关帝 Guāndì), to the Fire God (火神 Huǒshén), to the Wealth God (财神 Cáishén), temples of the City God (城隍神 Chénghuángshén), and at least one temple consecrated to the Yellow Deity of the Chariot Shaft (轩辕黄帝 Xuānyuán Huángdì) in Pinggu District. Many of these temples are governed by the Beijing Taoist Association, such as the Fire God Temple of the Shicha Lake, while many others are not and are governed by popular committees and locals. A great Temple of Xuanyuan Huangdi will be built in Pinggu (possibly as an expansion of the already existing shrine) within 2020, and the temple will feature a statue of the deity which will be amongst the tallest in the world.
The national Chinese Taoist Association and Chinese Taoist College have their headquarters at the White Cloud Temple of Quanzhen Taoism, which was founded in 741 and rebuilt numerous times. The Beijing Dongyue Temple outside Chaoyangmen is the largest temple of Zhengyi Taoism in the city. The local Beijing Taoist Association has its headquarters at the Lüzu Temple near Fuxingmen.
Buddhism

Beijing’s Tianning Temple, in Xicheng District.
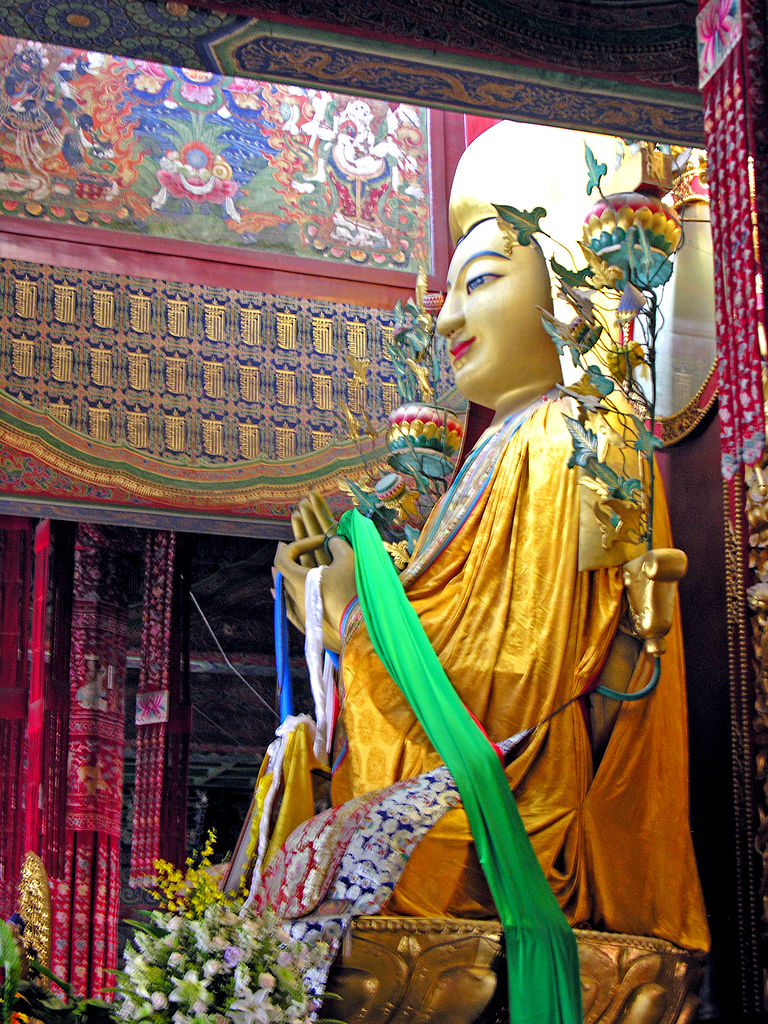

Altar of Tsongkhapa of the Hall of the Wheel of the Law of the Yonghe Temple of Tibetan Buddhism.
11% of the population of Beijing practices Buddhism. The Buddhist Association of China, the state’s supervisory organ overseeing all Buddhist institutions in mainland China, is headquartered in the Guangji Temple, a temple founded over 800 years ago during the Jin dynasty (1115–1234) in what is now Fuchengmennei. The Beijing Buddhist Association along with the Buddhist Choir and Orchestra are based in the Guanghua Temple, which dates to the Yuan Dynasty over 700 years ago. The Buddhist Academy of China and its library are housed in the Fayuan Temple near Caishikou. The Fayuan Temple, which dates to the Tang Dynasty 1300 years ago, is the oldest temple in urban Beijing. The Tongjiao Temple inside Dongzhimen is the city’s only Buddhist nunnery.
The West Yellow Temple originally dates to the Liao Dynasty. In 1651, the temple was commissioned by the Qing Emperor Shunzhi to host the visit of the Fifth Dalai Lama to Beijing. Since then, this temple has hosted the 13th Dalai Lama as well as the Sixth, Ninth and Tenth Panchen Lamas. The largest Tibetan Buddhist Temple in Beijing is the Yonghe Temple, which was decreed by the Qing Emperor Qianlong in 1744 to serve as the residence and research facility for his Buddhist preceptor of Rölpé Dorjé the third Changkya (or living Buddha of Inner Mongolia). The Yonghe Temple is so-named because it was the childhood residence of the Yongzheng Emperor, and retains the glazed tiles reserved for imperial palaces.
The Lingguang Temple of Badachu in the Western Hills also dates to the Tang Dynasty. The temple’s Zhaoxian Pagoda was first built in 1071 during the Liao Dynasty to hold a tooth relic of the Buddha. The pagoda was destroyed during the Boxer Rebellion and the tooth was discovered from its foundation. A new pagoda was built in 1964. The six aforementioned temples: Guangji, Guanghua, Tongjiao, West Yellow, Yonghe and Lingguang have been designated National Key Buddhist Temples in Han Chinese Area.
In addition, other notable temples in Beijing include the Tanzhe Temple (founded in the Jin dynasty (265–420) is the oldest in the municipality), Tianning Temple (oldest pagoda in the city), Miaoying Temple (famed for Yuan-era white dagoba), the Wanshou Temple (home to the Beijing Art Museum) and Big Bell Temple.
v t e | Buddhist temples in Beijing
Badachu . Bailin Temple . Big Bell Temple . Changchun Temple . Cheng’en Temple . Dahui Temple . Dajue Temple . Fahai Temple . Fayuan Temple . Guanghua Temple . Guangji Temple . Hongluo Temple . Jietai Temple . Miaoying Temple . Tanzhe Temple . Temple of Azure Clouds. Tianning Temple . Wanshou Temple . Wofo Temple . Xifeng Temple . Yonghe Temple . Yunju Temple . Zhenjue Temple . Zhihua Temple
Islam
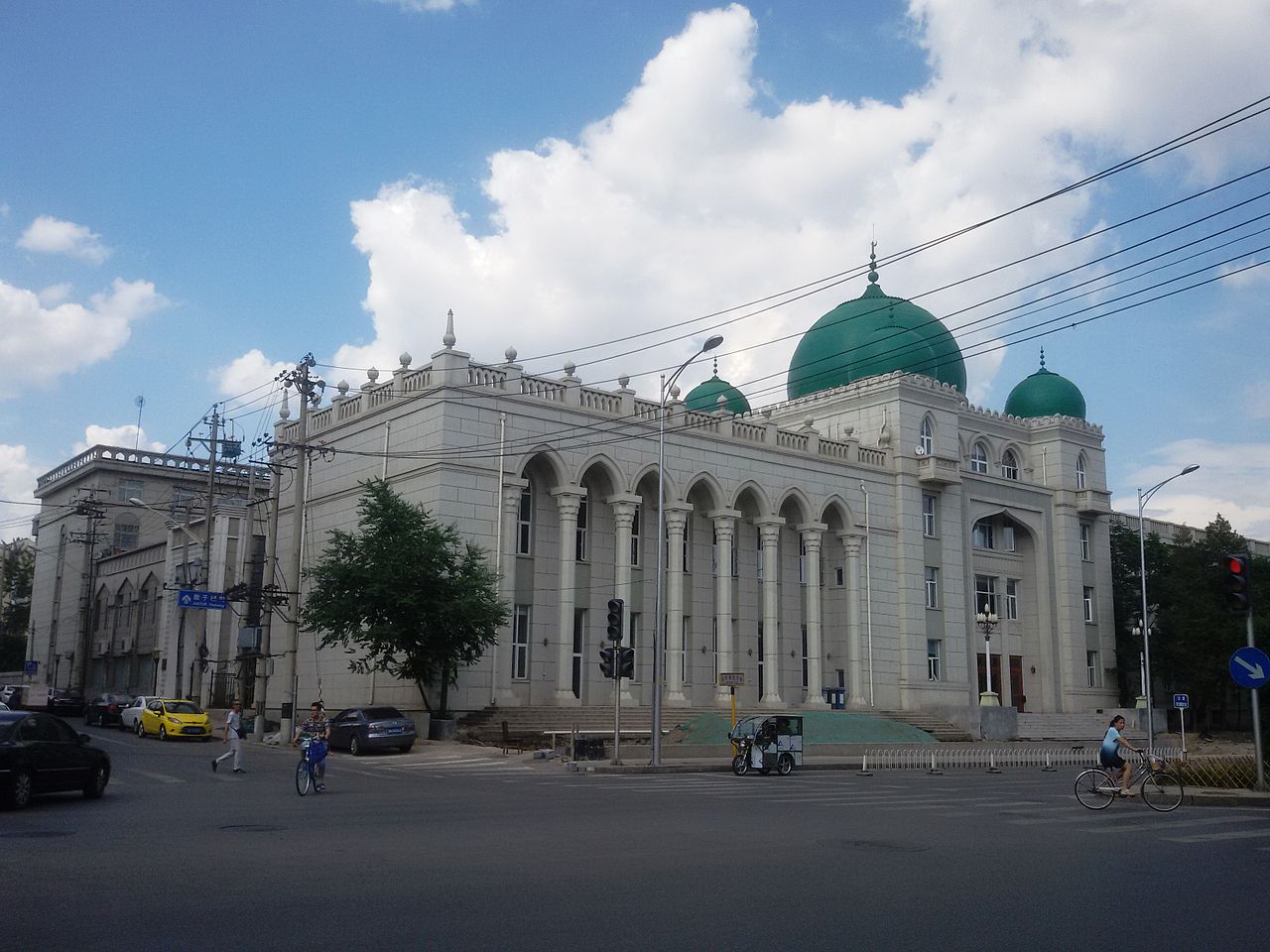

The headquarters of the Islamic Association of China near Niujie in Xicheng District.
Beijing has about 70 mosques recognized by the Islamic Association of China, whose headquarters are located next to the Niujie Mosque, the oldest and most famous mosque in the city. The Niujie Mosque was founded in 996 during the Liao Dynasty and is frequently visited by Muslim dignitaries. Other notable mosques in the old city include the Dongsi Mosque, founded in 1346; the Huashi Mosque, founded in 1415; Nan Douya Mosque, near Chaoyangmen; Jinshifang Street Mosque, in Xicheng District; and the Dongzhimen Mosque. There are large mosques in outlying Muslim communities in Haidian, Madian, Tongzhou, Changping, Changying, Shijingshan and Miyun. The China Islamic Institute is located in the Niujie neighborhood in Xicheng District.
Christianity
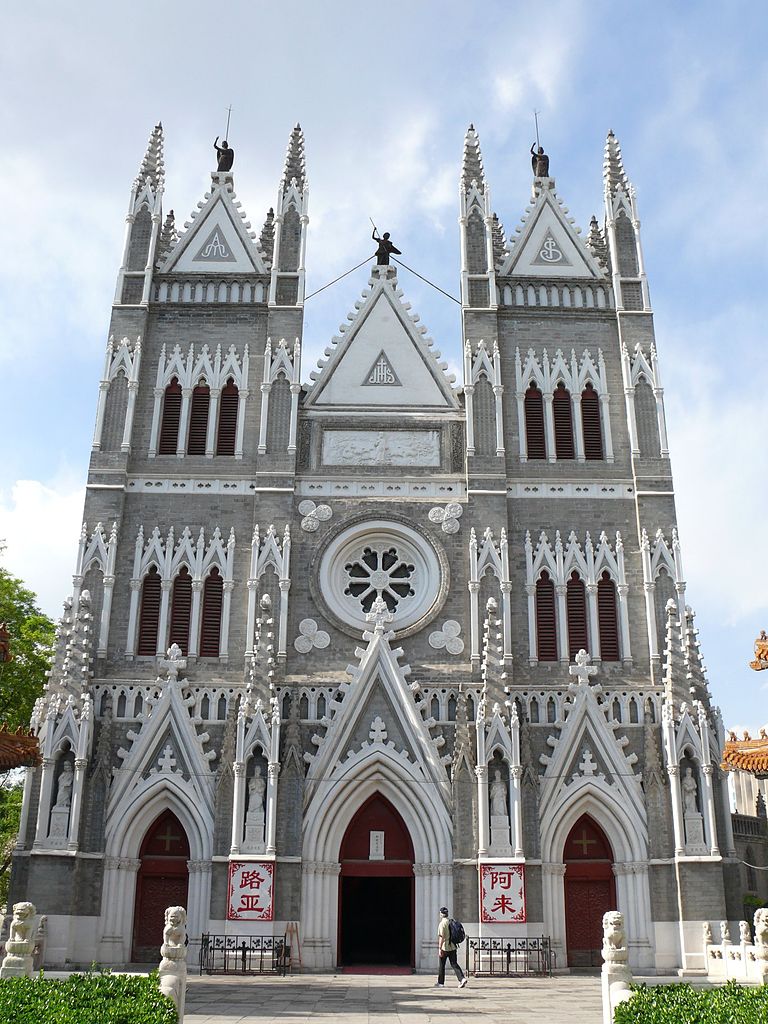

Church of the Saviour, also known as the Xishiku Church, founded in 1703.
Catholicism
In 1289, John of Montecorvino came to Beijing as a Franciscan missionary with the order from the Pope. After meeting and receiving the support of Kublai Khan in 1293, he built the first Catholic church in Beijing in 1305. The Chinese Patriotic Catholic Association (CPCA), based in Houhai is the government oversight body for Catholics in mainland China. Notable Catholic churches in Beijing include:
the Nantang or Cathedral of the Immaculate Conception also known as the Xuanwumen Church, which was founded in 1605 and whose current Archbishop Joseph Li Shan is one of the few bishops in China to have the support of both the Vatican and the CPCA.
the Dongtang or St. Joseph’s Church, better known as the Wangfujing Church, founded in 1653.
the Beitang or Church of the Saviour, also known as the Xishiku Church, founded in 1703.
the Xitang or Church of Our Lady of Mount Carmel also known as the Xizhimen Church, founded in 1723.
The National Seminary of Catholic Church in China is located in Daxing District.
Protestantism
The earliest Protestant churches in Beijing were founded by British and American missionaries in the second half of the 19th century. Protestant missionaries also opened schools, universities and hospitals which have become important civic institutions. Most of Beijing’s Protestant churches were destroyed during the Boxer Rebellion and rebuilt. In 1958, the 64 Protestant churches in the city were reorganized into four and overseen by the state through the Three-Self Patriotic Movement.
Eastern Orthodox
There were a significant amount of Orthodox Christian in Beijing. Orthodox has come to Beijing along with Russian prisoners from Albazino conflicts in the 17th century. In 1956, Viktor, the bishop of Beijing returned to the Soviet Union, and the Soviet embassy took over the old cathedral and demolished it. In 2007, Russian embassy has rebuilt a new church in its garden to serve the Russian Orthodox Christian in Beijing.
8 | Media
8.1 | Television and radio
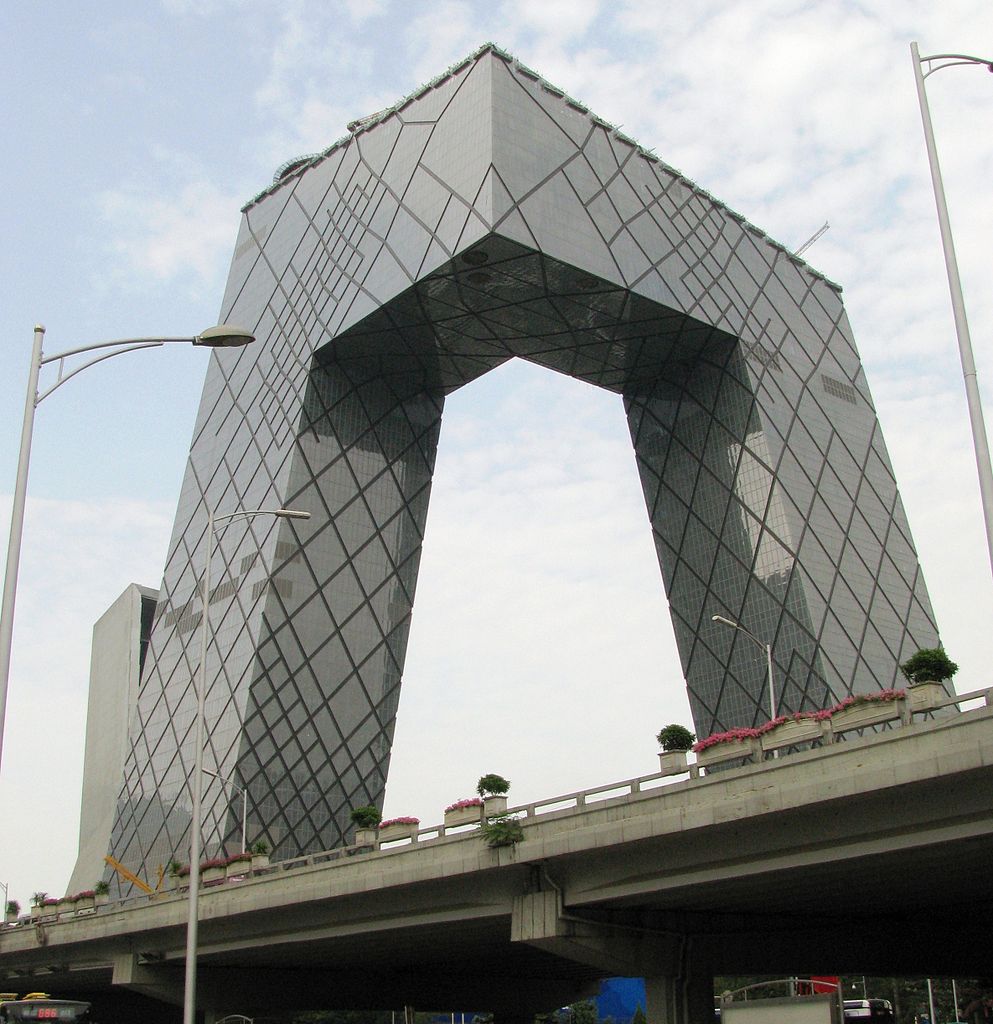

The China Central Television Headquarters building
Beijing Television broadcasts on channels 1 through 10, and China Central Television, China’s largest television network, maintains its headquarters in Beijing. Three radio stations feature programmes in English: Hit FM on FM 88.7, Easy FM by China Radio International on FM 91.5, and the newly launched Radio 774 on AM 774. Beijing Radio Stations is the family of radio stations serving the city.
8.2 | Press
The well-known Beijing Evening News (Beijing Wanbao, 北京晚报), covering news about Beijing in Chinese, is distributed every afternoon. Other newspapers include Beijing Daily, The Beijing News (Xin Jing Bao, 新京报), the Beijing Star Daily, the Beijing Morning News, and the Beijing Youth Daily (Beijing Qingnian Bao), as well as English-language weeklies Beijing Weekend and Beijing Today. The People’s Daily, Global Times and the China Daily (English) are published in Beijing as well.
Publications primarily aimed at international visitors and the expatriate community include the English-language periodicals Time Out Beijing, City Weekend, Beijing This Month, Beijing Talk, That’s Beijing, and The Beijinger.
9 | Sports
9.1 | Events

Fireworks above Olympic venues during the opening ceremony of the 2008 Summer Games

Tai chi (Taijiquan) practitioners at the Fragrant Hills Park
Beijing has hosted numerous international and national sporting events, the most notable was the 2008 Summer Olympic and Paralympic Games. Other multi-sport international events held in Beijing include the 2001 Universiade and the 1990 Asian Games. Single-sport international competitions include the Beijing Marathon (annually since 1981), China Open of Tennis (1993–97, annually since 2004), ISU Grand Prix of Figure Skating Cup of China (2003, 2004, 2005, 2008, 2009 and 2010), WPBSA China Open for Snooker (annually since 2005), Union Cycliste Internationale Tour of Beijing (since 2011), 1961 World Table Tennis Championships, 1987 IBF Badminton World Championships, the 2004 AFC Asian Cup (football), and 2009 Barclays Asia Trophy (football). Beijing hosted the 2015 IAAF World Championships in Athletics.
Beijing’s LeSports Center will be one of the main venues for the 2019 FIBA Basketball World Cup.
The city hosted the second Chinese National Games in 1914 and the first four National Games of China in 1959, 1965, 1975, 1979, respectively, and co-hosted the 1993 National Games with Sichuan and Qingdao. Beijing also hosted the inaugural National Peasants’ Games in 1988 and the sixth National Minority Games in 1999.
In November 2013, Beijing made a bid to host the 2022 Winter Olympics. On 31 July 2015, the International Olympic Committee awarded the 2022 Winter Olympics to the city.
9.2 | Venues
Major sporting venues in the city include the National Stadium, also known as the “Birds’ Nest”, National Aquatics Center, also known as the “Water Cube”, National Indoor Stadium, all in the Olympic Green to the north of downtown; the MasterCard Center at Wukesong west of downtown; the Workers’ Stadium and Workers’ Arena in Sanlitun just east of downtown and the Capital Arena in Baishiqiao, northeast of downtown. In addition, many universities in the city have their own sport facilities.
9.3 | Clubs
Professional sports teams based in Beijing include:
- China Baseball League
- Chinese Basketball Association
- Beijing Ducks
- Beikong Fly Dragons
- Women’s Chinese Basketball Association
- Chinese Super League
- Kontinental Hockey League
- China League One
- China League Two
- Chinese Women’s National League
The Beijing Olympians of the American Basketball Association, formerly a Chinese
Basketball Association team, kept their name and maintained a roster of primarily Chinese players after moving to Maywood, California in 2005.
China Bandy Federation is based in Beijing, one of several cities in which the potential for bandy development is explored.
10 | Transportation

Beijing Railway Station, one of several rail stations in the city

Traffic jam in the Beijing CBD

Terminal 3 of the Beijing Capital International Airport
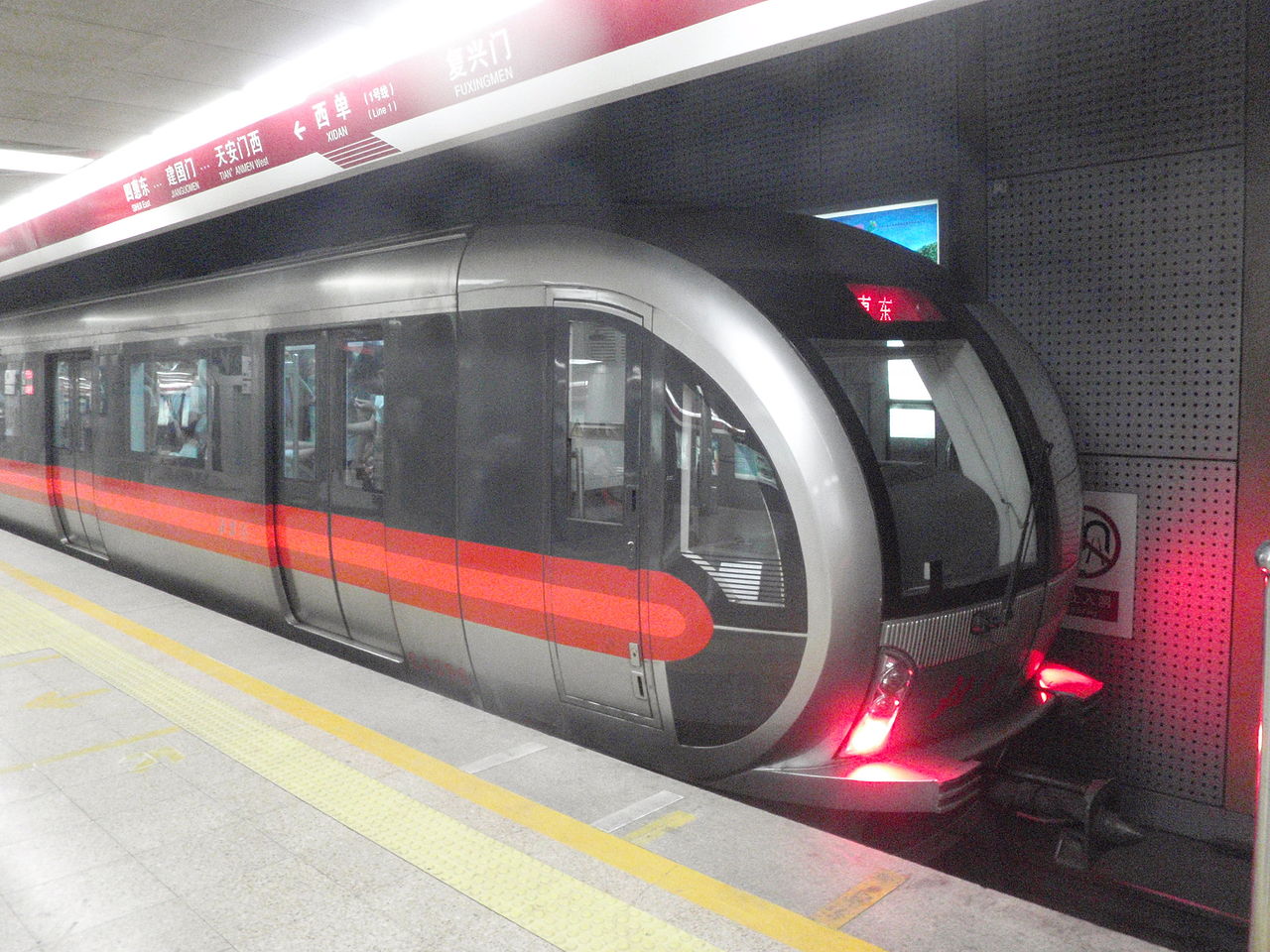

A Line 1 train on the Beijing Subway, which is among the longest and busiest rapid transit systems in the world.
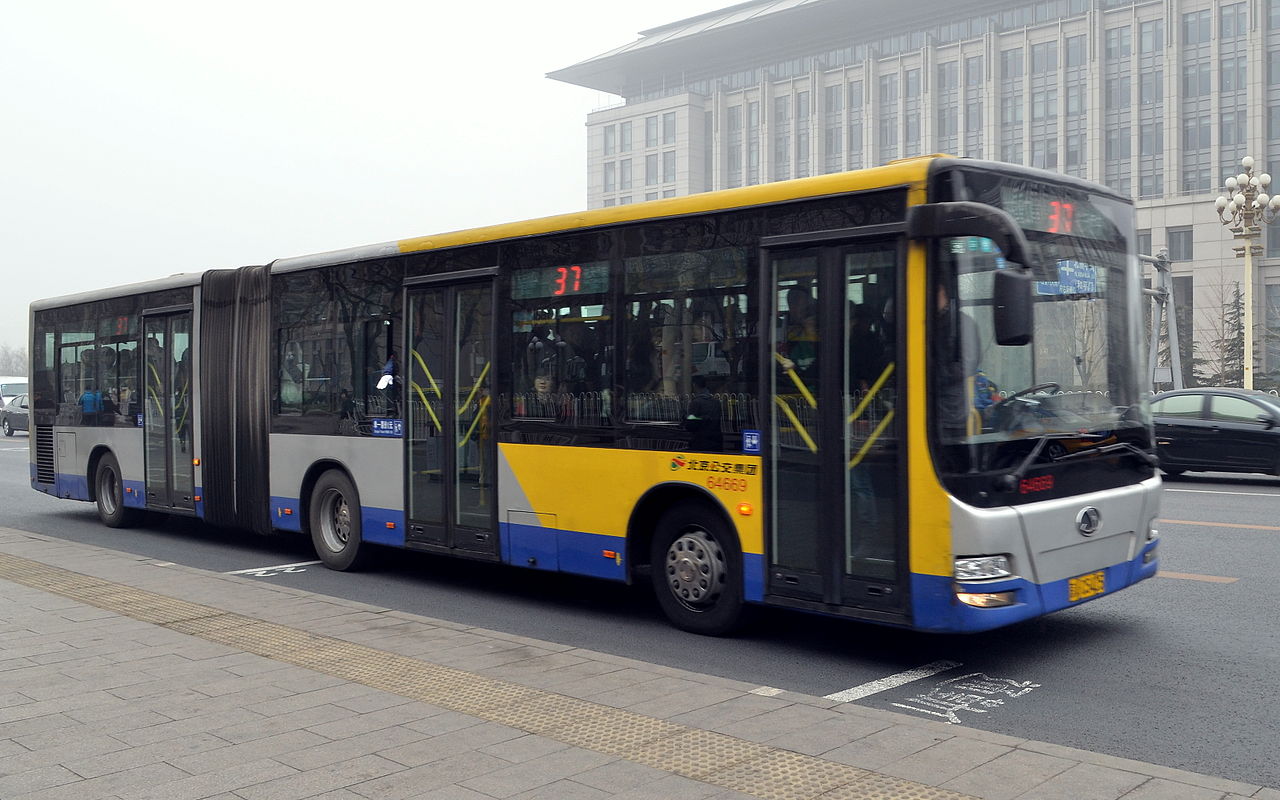

An articulated Beijing bus.
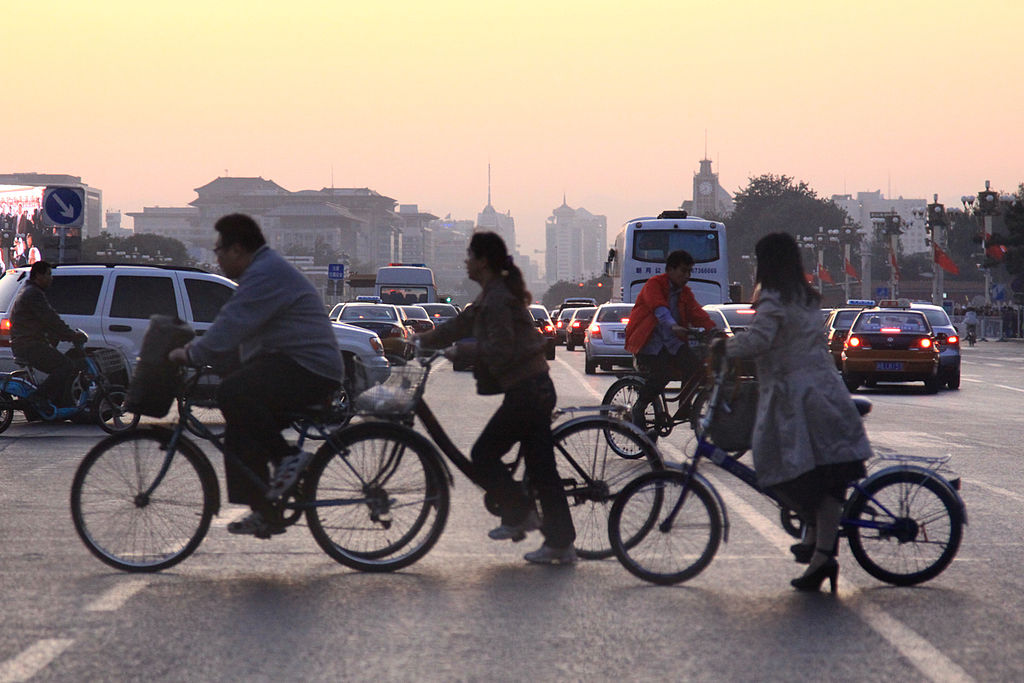

Bicyclists during rush hour at the Chang’an Avenue.

Typical Beijing traffic signage found at intersections.
Beijing is an important transport hub in North China with five ring roads, nine expressways, eleven National Highways, nine conventional railways, and two high-speed railways converging on the city.
10.1 | Rail and High-Speed Rail
Beijing serves as a large rail hub in China’s railway network. Ten conventional rail lines radiate from the city to: Shanghai (Jinghu Line), Guangzhou (Jingguang Line), Kowloon (Jingjiu Line), Harbin (Jingha Line), Baotou (Jingbao Line), Qinhuangdao (Jingqin Line), Chengde (Jingcheng Line), Tongliao, Inner Mongolia (Jingtong Line), Yuanping, Shanxi (Jingyuan Line) and Shacheng, Hebei (Fengsha Line). In addition, the Datong–Qinhuangdao Railway passes through the municipality to the north of the city.
Beijing also has three high-speed rail lines: the Beijing-Tianjin Intercity Railway, which opened in 2008; the Beijing-Shanghai High-Speed Railway, which opened in 2011; and the Beijing–Guangzhou High-Speed Railway, which opened in 2012.
The city’s main railway stations are the Beijing Railway Station, which opened in 1959; the Beijing West Railway Station, which opened in 1996; and the Beijing South Railway Station, which was rebuilt into the city’s high-speed railway station in 2008. As of 1 July 2010, Beijing Railway Station had 173 trains arriving daily, Beijing West had 232 trains and Beijing South had 163. The Beijing North Railway Station, first built in 1909 and expanded in 2009, had 22 trains.
Smaller stations in the city including Beijing East Railway Station and Qinghuayuan Railway Station handle mainly commuter passenger traffic. The Fengtai Railway Station has been closed for renovation. In outlying suburbs and counties of Beijing, there are over 40 railway stations.
From Beijing, direct passenger train service is available to most large cities in China. International train service is available to Mongolia, Russia, Vietnam and North Korea. Passenger trains in China are numbered according to their direction in relation to Beijing.
10.2 | Roads and Expressways
Beijing is connected by road links to all parts of China as part of the National Trunk Road Network. Nine expressways of China serve Beijing, as do eleven China National Highways. Beijing’s urban transport is dependent upon the five “ring roads” that concentrically surround the city, with the Forbidden City area marked as the geographical centre for the ring roads. The ring roads appear more rectangular than ring-shaped. There is no official “1st Ring Road”. The 2nd Ring Road is located in the inner city. Ring roads tend to resemble expressways progressively as they extend outwards, with the 5th and 6th Ring Roads being full-standard national expressways, linked to other roads only by interchanges. Expressways to other regions of China are generally accessible from the 3rd Ring Road outward. A final outer orbital, the Capital Ring Expressway (G95), is being built and will extend into neighbouring Tianjin and Hebei.
Within the urban core, city streets generally follow the checkerboard pattern of the ancient capital. Many of Beijing’s boulevards and streets with “inner” and “outer” are still named in relation to gates in the city wall, though most gates no longer stand. Traffic jams are a major concern. Even outside of rush hour, several roads still remain clogged with traffic.
Beijing’s urban design layout further exacerbates transportation problems. The authorities have introduced several bus lanes, which only public buses can use during rush hour. In the beginning of 2010, Beijing had 4 million registered automobiles. By the end of 2010, the government forecast 5 million. In 2010, new car registrations in Beijing averaged 15,500 per week.
Towards the end of 2010, the city government announced a series of drastic measures to tackle traffic jams, including limiting the number of new license plates issued to passenger cars to 20,000 a month and barring cars with non-Beijing plates from entering areas within the Fifth Ring Road during rush hour. More restrictive measures are also reserved during major events or heavily polluted weather.
10.3 | Air
Beijing’s primary airport is the Beijing Capital International Airport (IATA: PEK) about 20 kilometres (12 mi) northeast of the city centre. The airport is the second busiest airport in the world after Hartsfield-Jackson Atlanta International Airport. After renovations for the 2008 Olympics, the airport now boasts three terminals, with Terminal 3 being one of the largest in the world. Most domestic and nearly all international flights arrive at and depart from Capital Airport. It is the main hub for Air China and a hub for China Southern and Hainan Airlines. The airport links Beijing with almost every other Chinese city with regular air passenger service.
The Airport Expressway links the airport to central Beijing; it is a roughly 40-minute drive from the city centre during good traffic conditions. Prior to the 2008 Olympics, the 2nd Airport Expressway was built to the airport, as well as a light rail system, which now connects to the Beijing Subway.Other airports in the city include Liangxiang, Nanyuan, Xijiao, Shahe and Badaling. These airports are primarily for military use and are less well known to the public. Nanyuan serves as the hub for only one passenger airline. A second international airport, to be called Beijing Daxing International Airport, is currently being built in Daxing District, and is expected to be open by 2017.
As of 1 January 2013, tourists from 45 countries are permitted a 72-hour visa-free stay in Beijing. The 45 countries include Singapore, Japan, the United States, Canada, all EU and EEA countries (except Norway and Liechtenstein), Switzerland, Brazil, Argentina and Australia. The programme benefits transit and business travellers with the 72 hours calculated starting from the moment visitors receive their transit stay permits rather than the time of their plane’s arrival. Foreign visitors are not permitted to leave Beijing for other Chinese cities during the 72 hours.
10.4 | Public Transit
The Beijing Subway, which began operating in 1969, now has 19 lines, 345 stations, and 574 km (357 mi) of lines. It is the second longest subway system in the world and first in annual ridership with 3.66 billion rides delivered in 2016. In 2013, with a flat fare of ¥2.00 (0.31 USD) per ride with unlimited transfers on all lines except the Airport Express, the subway was also the most affordable rapid transit system in China. The subway is undergoing rapid expansion and is expected to reach 30 lines, 450 stations, 1,050 kilometres (650 mi) in length by 2020. When fully implemented, 95% of residents inside the Fourth Ring Road will be able to walk to a station in 15 minutes. The Beijing Suburban Railway provides commuter rail service to outlying suburbs of the municipality.
On December 28, 2014, the Beijing Subway switched to a distance-based fare system from a fixed fare for all lines except the Airport Express. Under the new system a trip under 6 km will cost ¥3.00(0.49 USD), an additional ¥1.00 will be added for the next 6 kilometres (3.7 miles) and the next 10 kilometres (6.2 miles) until the distance for the trip reaches 32 kilometres (20 miles). For every 20 kilometres (12 miles) after the original 32 kilometres (20 miles) an additional ¥1.00 is added. For example, a 50 kilometres (31 miles) trip would cost ¥ 8.00.
There are nearly 1,000 public bus and trolleybus lines in the city, including four bus rapid transit lines. Standard bus fares are as low as ¥1.00 when purchased with the Yikatong metrocard.
10.5 | Taxi
Metered taxi in Beijing start at ¥13 for the first 3 kilometres (1.9 mi), ¥2.3 Renminbi per additional 1 kilometre (0.62 mi) and ¥1 per ride fuel surcharge, not counting idling fees which are ¥2.3 (¥4.6 during rush hours of 7–9 am and 5–7 pm) per 5 minutes of standing or running at speeds lower than 12 kilometres per hour (7.5 mph) . Most taxis are Hyundai Elantras, Hyundai Sonatas, Peugeots, Citroëns and Volkswagen Jettas. After 15 kilometres (9.3 mi), the base fare increases by 50% (but is only applied to the portion over that distance). Different companies have special colours combinations painted on their vehicles. Usually registered taxis have yellowish brown as basic hue, with another color of Prussian blue, hunter green, white, umber, tyrian purple, rufous, or sea green. Between 11 pm and 5 am, there is also a 20% fee increase. Rides over 15 km (9 mi) and between 23:00 and 06:00 incur both charges, for a total increase of 80%. Tolls during trip should be covered by customers and the costs of trips beyond Beijing city limits should be negotiated with the driver. The cost of unregistered taxis is also subject to negotiation with the driver.
10.6 | Bicycles
Beijing has long been well known for the number of bicycles on its streets. Although the rise of motor traffic has created a great deal of congestion and bicycle use has declined, bicycles are still an important form of local transportation. Large numbers of cyclists can be seen on most roads in the city, and most of the main roads have dedicated bicycle lanes. Beijing is relatively flat, which makes cycling convenient. The rise of electric bicycles and electric scooters, which have similar speeds and use the same cycle lanes, may have brought about a revival in bicycle-speed two-wheeled transport. It is possible to cycle to most parts of the city. Because of the growing traffic congestion, the authorities have indicated more than once that they wish to encourage cycling, but it is not clear whether there is sufficient will to translate that into action on a significant scale. Recently, cycling has seen a resurgence in popularity thanks to the emergence of a large number of dockless app based bikeshares such as Mobike, Bluegogo and Ofo.
11 | Defense and Aerospace
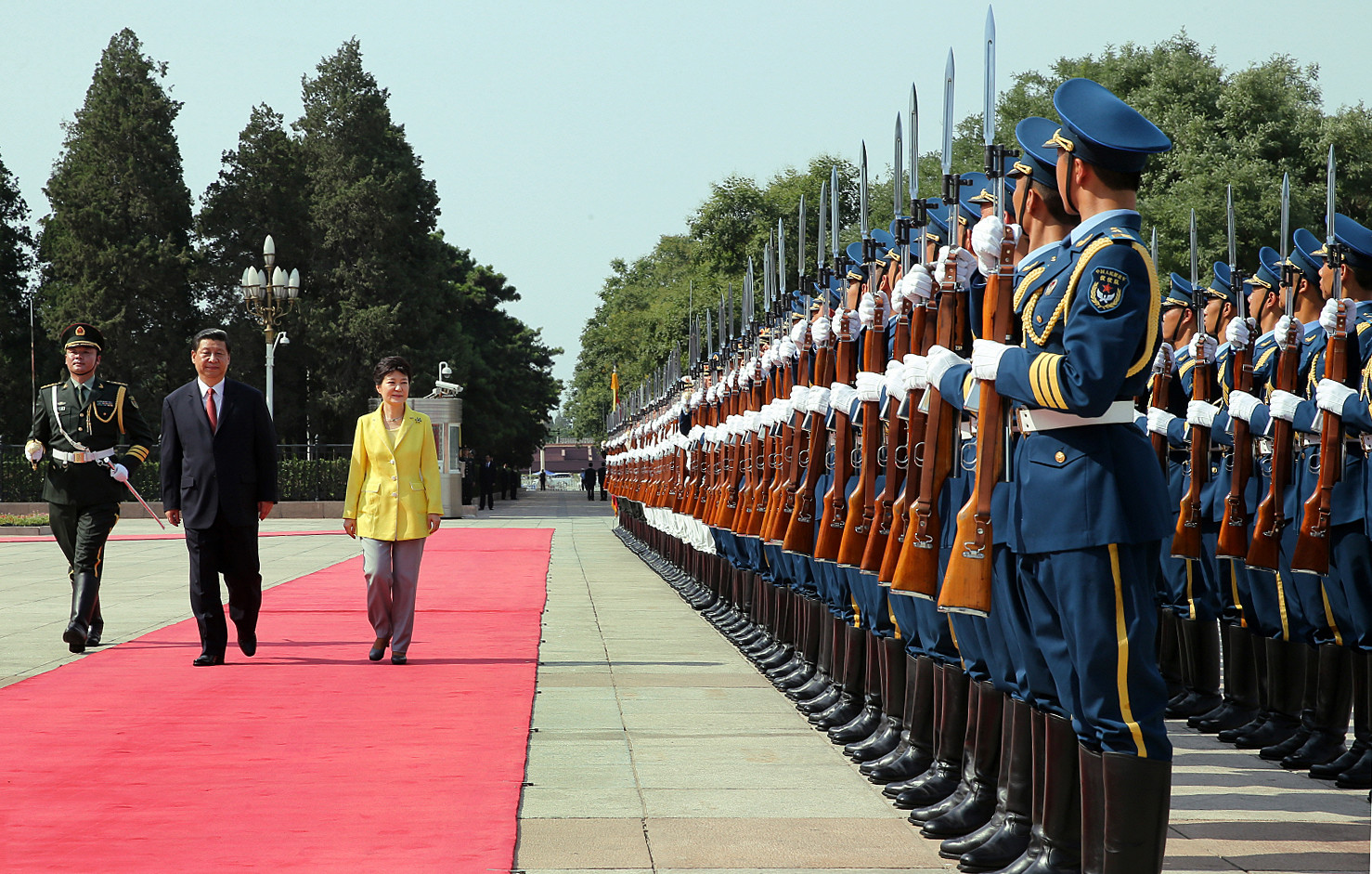

Chinese President Xi Jinping and a military honor guard welcomes South Korean president Park Geun-hye in June 2013.
The command headquarters of China’s military forces are based in Beijing. The Central Military Commission, the political organ in charge of the military, is housed inside the Ministry of National Defense, located next to the Military Museum of the Chinese People’s Revolution in western Beijing. The Second Artillery Corps, which controls the country’s strategic missile and nuclear weapons, has its command in Qinghe, Haidian District. The headquarters of the Beijing Military Region, one of seven nationally, is based further west in Gaojing. The Beijing Military Region oversees the Beijing Garrisons as well as the 27th, 38th and 65th Armies, which are based in Hebei.
Military institutions in Beijing also include academies and thinktanks such as the PLA National Defence University and Academy of Military Science, military hospitals such as the 301, 307 and the Academy of Military Medical Sciences, and army-affiliated cultural entities such as the 1 August Film Studios and the PLA Song and Dance Troupe.
The China National Space Administration, which oversees country’s space program, and several space-related state owned companies such as CASTC and CASIC are all based in Beijing. The Beijing Aerospace Command and Control Center, in Haidian District tracks the country’s manned and unmanned flight and other space exploration initiatives.
12 | Nature and Wildlife
Beijing Municipality has 20 nature reserves that have a total area of 1,339.7 km2 (517.3 sq mi). The mountains to the west and north of the city are home to a number of protected wildlife species including leopard, leopard cat, wolf, red fox, wild boar, masked palm civet, raccoon dog, hog badger, Siberian weasel, Amur hedgehog, roe deer, and mandarin rat snake. The Beijing Aquatic Wildlife Rescue and Conservation Center protects the Chinese giant salamander, Amur stickleback and mandarin duck on the Huaijiu and Huaisha Rivers in Huairou District. The Beijing Milu Park south of the city is home to one of the largest herds of Père David’s deer, now extinct in the wild. The Beijing barbastelle, a species of vesper bat discovered in caves of Fangshan District in 2001 and identified as a distinct species in 2007, is endemic to Beijing. The mountains of Fangshan are also habitat for the more common Beijing mouse-eared bat, large myotis, greater horseshoe bat and Rickett’s big-footed bat.
Each year, Beijing hosts 200-300 species of migratory birds including the common crane, black-headed gull, swan, mallard, common cuckoo and the endangered yellow-breasted bunting. In May 2016, Common cuckoos nesting in the wetlands of Cuihu (Haidian), Hanshiqiao (Shunyi), Yeyahu (Yanqing) were tagged and have been traced to far as India, Kenya and Mozambique. In the fall of 2016, the Beijing Forest Police undertook a month-long campaign to crack down on illegal hunting and trapping of migratory birds for sale in local bird markets. Over 1,000 rescued birds of protected species including streptopelia, Eurasian siskin, crested myna, coal tit and great tit were handed to the Beijing Wildlife Protection and Rescue Center for repatriation to the wild.
The city flowers are the Chinese rose and chrysanthemum. The city trees are the Chinese arborvitae, an evergreen in the cypress family and the Pagoda Tree, also called the Chinese scholar tree, a deciduous tree of the Fabaceae family. The oldest scholar tree in the city was planted in what is now Beihai Park during the Tang Dynasty, 1,300 years ago.